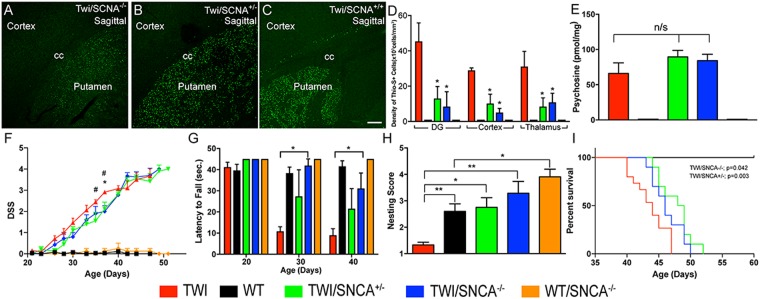
Figure 1.
Knock-out of SNCA removes thioflavin-S-positive inclusions in certain brain regions and improves survival and behavior of TWI mice. (A) Brain tissue from TWI/SCNA−/− (A), TWI/SCNA+/− (B) and TWI/SCNA+/+ (C) were stained for thioflavin-S-positive protein aggregates. Thio-S material was visibly reduced in the lower cortical layers and putamen of TWI/SNCA−/− brains (A) and TWI/SNCA+/− brains (B) with respect to TWI/SNCA+/+ (C). Images (A–C) show anatomical regions encompassing deep cerebral cortex and the putamen. cc, corpus callosum. Scale bar = 200 μm. (D) Unbiased stereology quantitatively revealed a significantly reduced abundance of thio-S+ material in TWI/SNCA−/− and TWI/SNCA+/− brains (p = 0.001, ANOVA) within the Dentate Gyrus (DG), Cerebral Cortex (Cortex), and Thalamus. (E) Psychosine levels measured using LC-MS-MS showed non-significant (n/s) changes between the presence or absence of the SCNA allele in TWI brains. (F) A disease severity score (DSS) measured less severe signs in TWI/SNCA+/− and TWI/SNCA−/− mice compared to TWI/SNCA+/+, while changes were significant at only P36 and P38 for TWI/SNCA+/− (*p < 0.05) and P36 for TWI/SNCA−/− (*p < 0.05). (G) Grip strength, as assessed by a latency-to-fall test, was significantly improved in TWI/SNCA−/− compared to TWI/SNCA+/+ at P30 (*p < 0.05). (H) Nesting ability score, assessed at P20 in each genotype group, was significantly improved in both TWI/SNCA+/− and TWI/SNCA−/− compared to TWI mice (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ANOVA). (I) Kaplan-Meier survival curves reveal significantly longer life of TWI/SNCA+/− and TWI/SNCA−/− compared to TWI. N = 10 mice (TWI/SNA+/− and TWI/SNCA−/−) N = 15 mice (TWI/SNCA+/+).