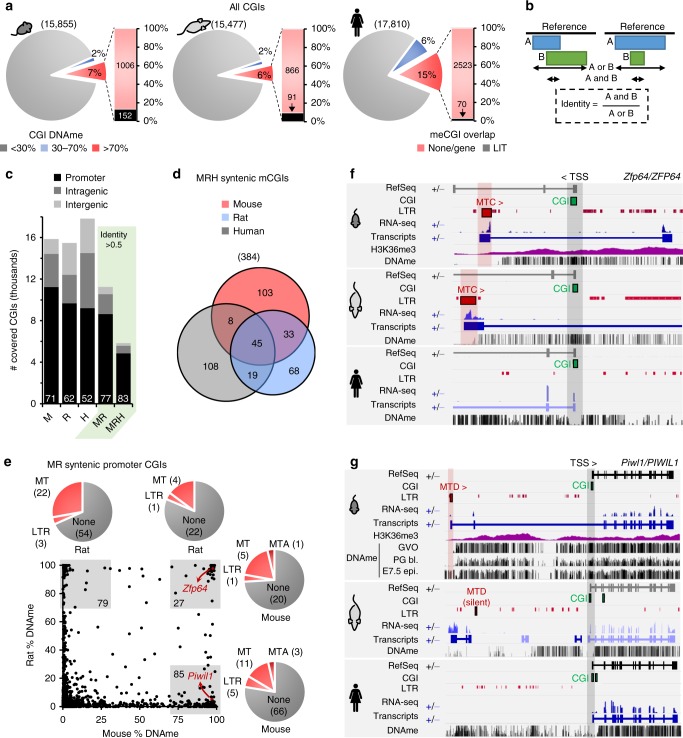
Fig. 4.
LTR transcription leads to species- and rodent-specific CpG island (CGI) methylation. a Proportion of CGIs (>5 CpGs covered by WGBS) with low (<30%), intermediate (30–70%), or high (>70%) DNAme levels in mouse, rat, and human oocytes. The proportion and number of hypermethylated CGIs embedded within an LIT is depicted in the accompanying bar chart (black). b Identification of syntenic CGIs between two species by calculation of identity. CGIs with an identity >0.5 between two species were included in our analyses. c Proportion of CGIs overlapping with an annotated TSS (±500 bp; promoter CGIs), gene body (intragenic), or intergenic region in human (H), mouse (M), rat (R), mouse + rat (MR), and mouse + rat + human (MRH). Total number of CGIs with >5 CpGs >5× WGBS coverage in each species and subset of CGIs syntenic (identity >0.5) between mouse (M) and rat (R) or all three species are shown. The percentage of CGIs overlapping a TSS is also shown for each. d Venn diagram showing the overlap in DNAme at all syntenic CGIs hypermethylated in in at least one of mouse, rat, or human oocytes (384). e Syntenic promoter CGIs hypermethylated in mouse and/or in rat oocytes (gray boxes). The proportion of meCGIs that overlap with a transcript initiated in an MTA, a non-MTA MT element (MTB, MTC, MTD, or MTE), or a non-MT LTR element is depicted in the adjacent pie charts. f Genome browser screenshots of the Zfp64 CGI promoter. In mouse and rat oocytes, an MTC-driven antisense LIT overlapping the canonical promoter CGI appears to be responsible for DNAme, consistent with the H3K36me3 profile in mouse oocytes. g Screenshot of the Piwil1 locus illustrating transcription and DNAme in mouse, rat, and human oocytes. H3K36me3 in oocytes and DNAme in PG blastocysts and E7.5 embryos are also shown for mouse. A mouse-specific Piwil1 LIT initiates in an MTD element situated upstream of the canonical TSS, and only the mouse CGI promoter is hypermethylated. Mouse and human WGBS datasets analyzed from refs. 12,16 and human RNA-seq data from ref. 17