Figure 1.
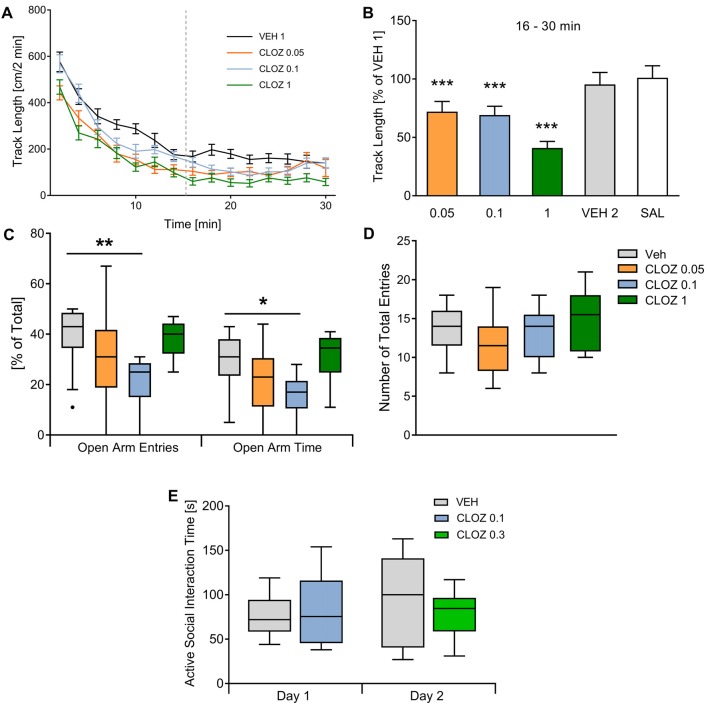
Clozapine/CLOZ reduces locomotor activity and induces an anxious phenotype but does not affect social interaction. (A) Locomotor activity: directly after placing rats (n = 19) in the open field, they showed high locomotor activity and reached a steady state after 15 min (data of the second vehicle injection/VEH 2 and saline/SAL were not different from VEH and are not shown to improve readability of the figure). (B) Track length in all conditions is expressed as percentage of the VEH 1 baseline value. For this steady-state activity, track length was affected by subject (repeated-measures one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test; F(18,90) = 8.85; p = 3 × 10−13) and treatment (F(5,90) = 16.34; p = 2 × 10−11). We observed a dose-dependent decrease after low-dose CLOZ administration (all compared against VEH injection). The lowest doses used caused similar decreases in track length (0.1 mg/kg CLOZ: p = 2 × 10−4, this corresponds to 69.2 ± 7.5% of the track length after VEH injection; 0.05 mg/kg CLOZ: p = 10−4; 72.1 ± 8.73%). There was an even stronger reduction with 1 mg/kg CLOZ (p < 10−4; 40.9 ± 5.7%). The second vehicle (VEH 2) injection was performed to test if repetition influences steady-state activity, but no difference was observed (p = 0.27; 95.4 ± 10.2%). Also, SAL treatment didn’t change the track length (p = 0.56; 101.1 ± 10.2%). Data are represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). (C,D) Elevated plus-maze: the percentage of open arm entries/%OAE (H = 13.0, p = 0.0046, Kruskal-Wallis test) and the percentage of open arm time/%OAT (H = 11.3, p = 0.010, Kruskal-Wallis test) was different between groups. Post hoc tests showed that the dose of 0.1 mg/kg induced an anxious phenotype. Both the %OAE (p = 0.023, Dunn’s multiple comparisons test) and %OAT (p = 0.023) were decreased with this dose (n = 9). 0.05 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg CLOZ did not affect the %OAE or the %OAT significantly. The total number of entries (controlling for locomotor activity effects) were not different between groups (p = 0.24, Kruskal-Wallis test). (E) Social interaction: no significant differences concerning cumulative active social interaction time were observed with both doses tested (0.1 mg/kg and 0.3 mg/kg CLOZ, p = 0.99 and p = 0.57, n = 10 per group). Data displayed as median and the first and third quartile (P25, P75; Tukey-style whiskers) *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.