Fig. 6.
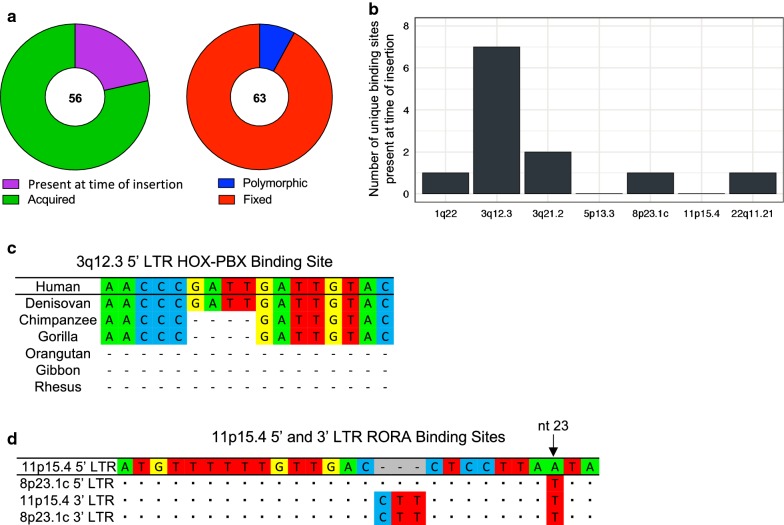
Characterization of unique transcription factor binding sites. a Pie charts describing the unique binding sites in the 5′ and 3′ LTRs of proviruses in this study. Shown is the number of unique binding sites that were either present at the time of insertion or acquired over time (left) as well as the number of unique binding sites that are either polymorphic or fixed in the human population (right). b The number of unique transcription factor binding sites identified as being present at the time of insertion found on each 5′ LTR of interest in this study. c Multiple sequence alignment of the human HOX-PBX binding site in the 3q12.3 5′ LTR as compared to the homologous sequences in different non-human primate reference genomes. Dashes indicate indels. d Multiple sequence alignment of the RORA binding site in the 11p15.4 5′ and 3′ LTRs as compared to the 5′ and 3′ LTRs of the 8p23.1c provirus. Dots are used for shared identity and dashes indicate indels. The nucleotide that appears to be responsible for the RORA functional polymorphism, is shown with an arrow