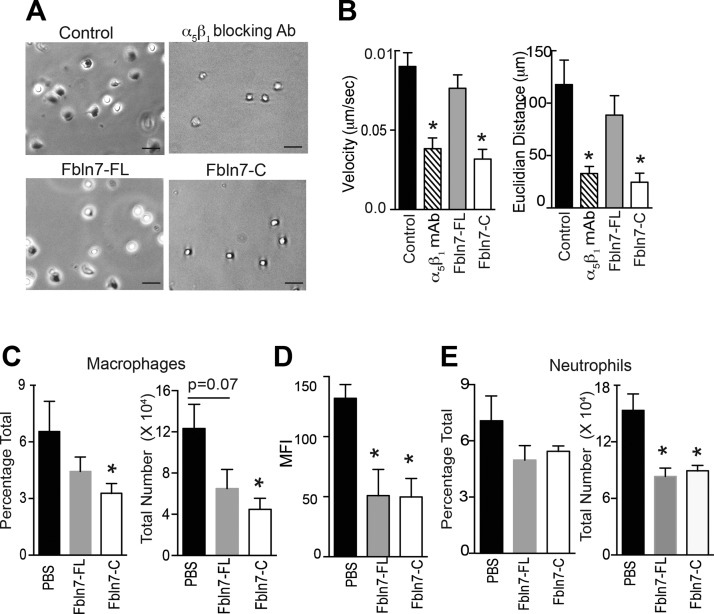
Figure 4.
Fbln7-C inhibits the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) –mediated migration of activated monocytes on fibronectin in vitro and reduces macrophage infiltration into inflamed tissues in vivo. Cell migration of TNF-α–stimulated monocytes on fibronectin in response to MCP-1 was performed by using time-lapse video microscopy. A) Snapshot from the live cell migration assay of TNF-α–activated human monocytes on fibronectin in response to MCP-1. Cells were pretreated with α5β1 blocking Ab (upper right), Fbln7-FL (20 µg/ml; lower left), and Fbln7-C (20 µg/ml; lower right) before plating cells on fibronectin-coated dishes. Scale bars, 50 µm. B) Velocity and Euclidian distance (length of straight line between the initial and final points) of the attached cells were quantified by using the manual tracking and chemotaxis tool in ImageJ (n = 11/group). C–E) Cells were isolated from peritoneal lavage and lungs of endotoxemic mice (18 h after LPS injection) that were administered PBS, Fbln7-FL (10 μg/dose i.v.), or Fbln7-C (10 μg/dose i.v.) in 2 doses at 1 and 4 h. Anti-F4/80, anti-CD11b, anti-Ly6G, and anti–MHC-II Abs were used for staining. FVS450− cells were gated (live cells) for analysis. C) Bar graph shows the frequencies and total number of macrophages (F4/80) in the peritoneal lavage. D) Bar graph shows the mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) of MHC-II expression on macrophages in the peritoneal lavage. E) Bar graph shows the frequencies and total number of neutrophils (CD11bhiLy6Ghi) in the peritoneal lavage (n = 4/group for PBS and Fbln7-C groups; n = 3 for the Fbln7-FL group). Results are expressed as means ± sem. *P < 0.05.