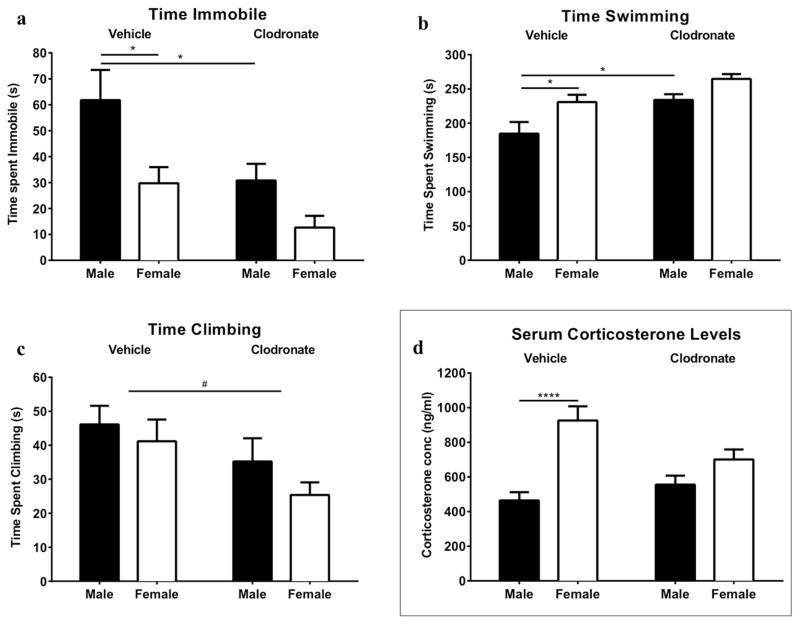
Figure 10. Adult forced-swim test and acute stress responsivity.
Forced-swim test behavioral measures included a) time spent immobile, b) time swimming, c) time climbing. Vehicle male rats spent more time immobile than vehicle female rats and clodronate male rats (a). Clodronate rats spent less time climbing than vehicle rats (b). Vehicle male rats spent significantly less time swimming than vehicle female rats and clodronate male rats (c). Corticosterone levels after acute restraint stress (d). Corticosterone levels were normalized to one sample that was run on both plates for a cross-plate comparison. Vehicle treated females had higher levels of corticosterone compared to vehicle treated males after acute restraint stress. *p < 0.05, ****p < 0.0001, #p < 0.05 between treatment, n = 9 for clodronate treated males, n = 10 for vehicle treated males, n = 11 for clodronate treated and vehicle treated females.