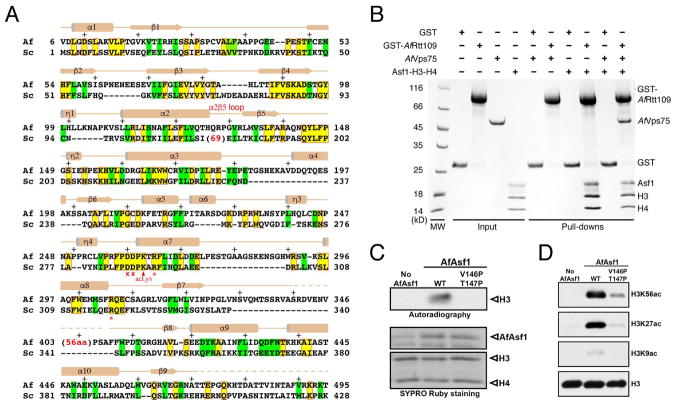
Figure 1. Sequence and functional conservation of Rtt109.
(A) Structure-based alignment of A. fumigatus and S. cerevisiae Rtt109 catalytic core sequences. Identical and similar residues are highlighted yellow (boxed in red) and green, respectively. The asterisks and crosses indicate residues interacting with H3E94 and those lining the H3K56 entry channel, respectively. Auto-acetylated Lys263 is also labeled. Above the sequences, secondary structural elements of AfRtt109 are superimposed; “+” signs mark every ten residues. (B) GST-pulldown of AfRtt109 in the presence of the AfAsf1-H3-H4 complex or a putative AfVps75 homolog. (C) Autoradiograph of the HAT activities of AfRtt109 using WT or mutant AfAsf1 in complex with histones H3-H4 as the substrate. (D) Detection of H3K56ac, H3K27ac and H3K9ac in the in vitro HAT assay by Western blot analysis using AfRtt109 as the enzyme and WT or mutant AfAsf1 in complex with histones H3-H4 as the substrate. See also Figure S6; Table S3.