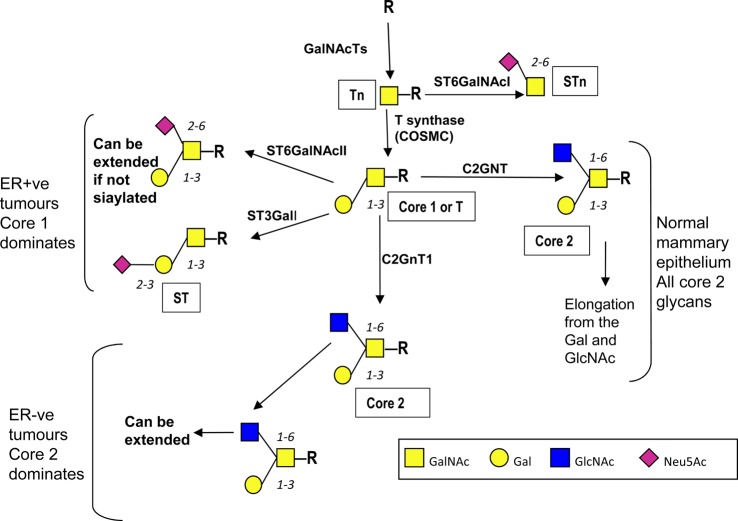
Figure 1. Pathways of O-GaalNAc glycosylation in the normal and malignant mammary gland.
In the normal mammary gland epithelial cells O-GalNAc glycans are core 2-based and extension can occur from the Gal and the GlcNAc. COSMC is indicated under the T synthase as it acts as a private chaperone for this enzyme and hence is required for T synthase activity ([21], see text). In many breast cancers truncated mucin-type O-linked glycans are seen often terminating in sialic acid due to up-regulation of sialyltransferases [16]. However, in ER-ve breast cancer core 2-based glycans are expected to be present and may dominate due to the overexpression of the C1GALT1 and GCNT1 in ER-ve tumours compared with ER+ve breast cancers [20]. Symbols used are based on the nomenclature recommended in Varki et al. [79].