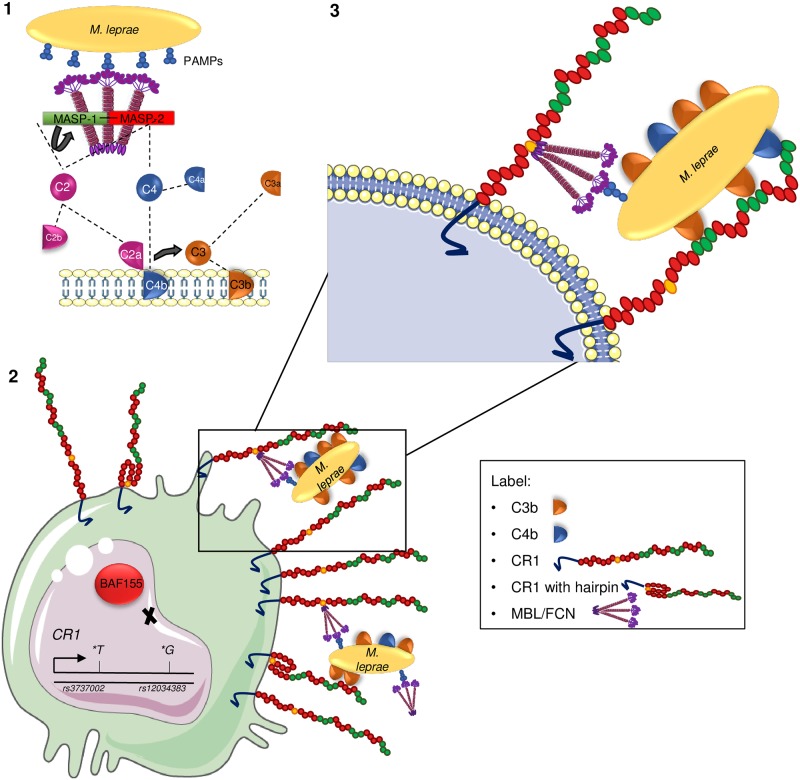
Fig 5. CR1 possible roles on leprosy susceptibility.
(1) Pathogen or damage-associated molecular sugar patterns (PAMPs/DAMPs) on Mycobacterium leprae are recognized by mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins (FCNs) and activate the lectin pathway of complement. Autoactivation of the serine protease MASP-1 is followed by transactivation of MASP-2, cleavage of C2 and C4 and formation of the C3 convertase C2aC4b. C3 convertase ultimately leads to the insertion of C3b opsonins on the surface of the pathogen. (2) Macrophages presenting rs3737002*T (p.1408Met) may produce CR1 molecules whose enzymatic cleavage site is hidden, producing less soluble CR1 molecules. Those with rs12034383*G present lower affinity for BAF155-containing SWI/SNF nucleosome remodelling complex, increasing CR1 gene expression. (3) Increased CR1 abundance is expected to enhance the uptake of C3b/C4b/ficolin/MBL-opsonized M. leprae, through the respective SCR (short consensus repeat) domains (shown in green and yellow).