Figure 1.
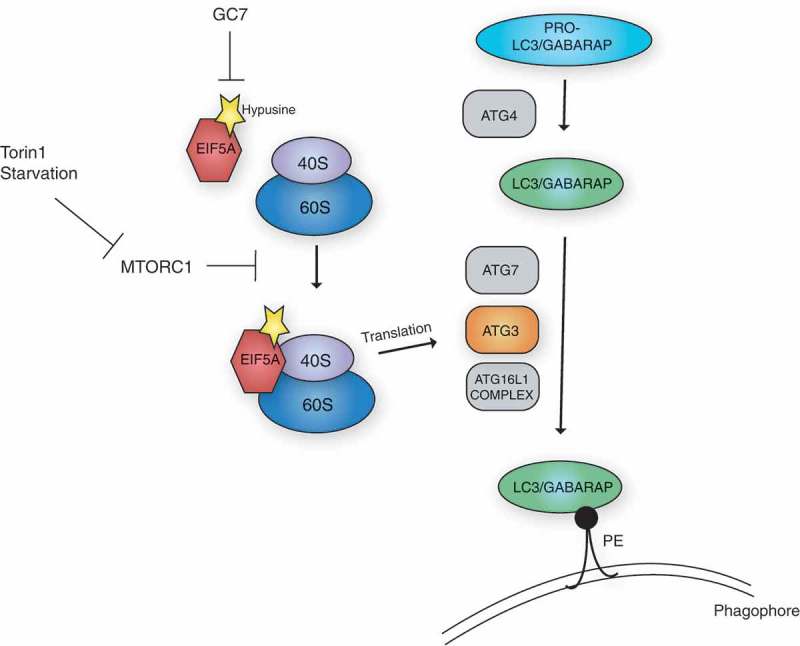
EIF5A is required for autophagy via the translation of ATG3. The LC3/GABARAP proteins are processed, first by ATG4, and subsequently by the lipidation machinery, including the E1-like ATG7, the E2-like ATG3 and the E3-like ATG16L1 complex. This results in their lipidation and anchoring to the phagophore membrane via phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), which is required for autophagy. EIF5A, via a hypusine-dependent mechanism, can associate with the ribosome and assist in the translation of ATG3. Stimulation of autophagy by MTORC1 inhibition (via starvation or Torin1 treatment), can enhance EIF5A association with the ribosome. Inhibition of hypusination by treatment with N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7), can effectively inhibit this process.
