Figure 6.
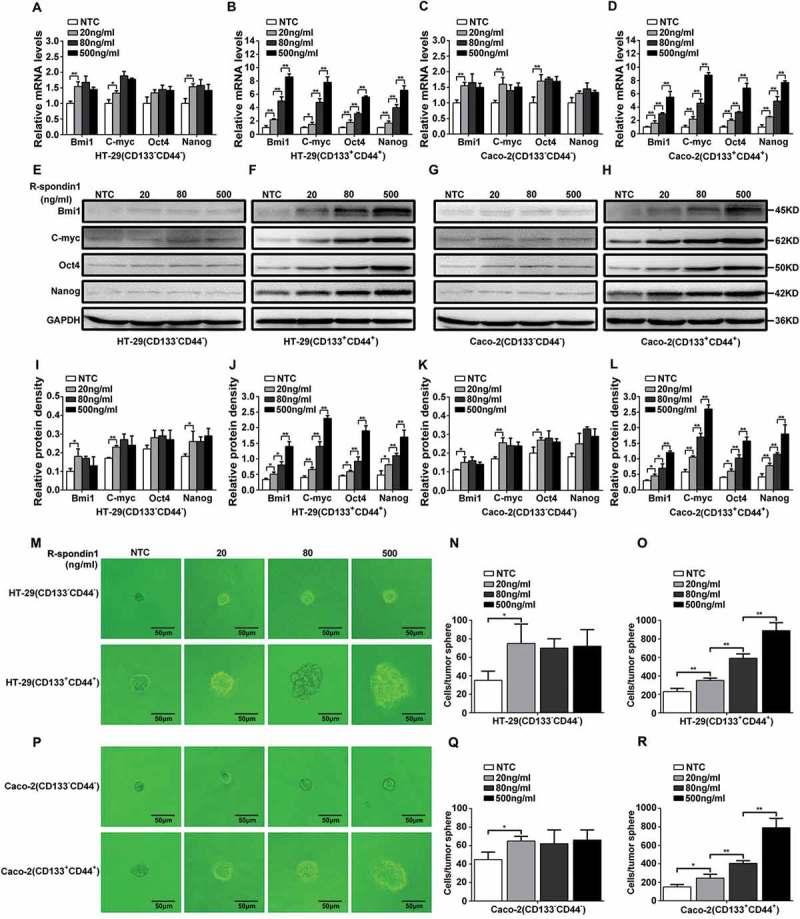
Expression of “stemness”-associated genes and tumorsphere formation in CD133+CD44+ and CD133−CD44− CRC cell populations treated with hRspo1. (A-D) Expression of “stemness”-associated genes (mRNA) in CD133+CD44+ (B and D) and CD133−CD44− (A and C) CRC cell populations from HT-29 and LS174T cells treated with 20, 80 or 500 ng/ml hRspo1. (E-H) Expression of “stemness”-associated genes (protein) in CD133+CD44+ (F and H) and CD133−CD44− (E and G) CRC populations treated with hRspo1. (I-L) The lower panel shows the quantitation of western blots (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01). (M-R) CD133+CD44+ and CD133−CD44− CRC cell populations were treated with 20, 80 or 500 ng/ml hRspo1 and cultured in a special ultra-low attachment culture plate with conditional medium for tumorsphere formation. Tumorspheres formed in CD133+CD44+ HT-29 or Caco-2 cells were larger than those formed in CD133−CD44− HT-29 or Caco-2 cells (M and P). The cell numbers per tumorsphere formed in 20 ng/ml hRspo1-treated CD133−CD44− HT-29 or Caco-2 cells were more than for the non-treated control (NTC), but there were no significant differences among 20, 80 or 500 ng/ml hRspo1-treated CD133−CD44− HT-29 or Caco-2 cells (N and Q). The cell numbers per tumorsphere formed in 20, 80 or 500 ng/ml hRspo1-treated CD133+CD44+ CRC cell populations were more than in the non-treated control (NTC) and increased significantly in a dose-dependent manner (*: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01) (O and R).
