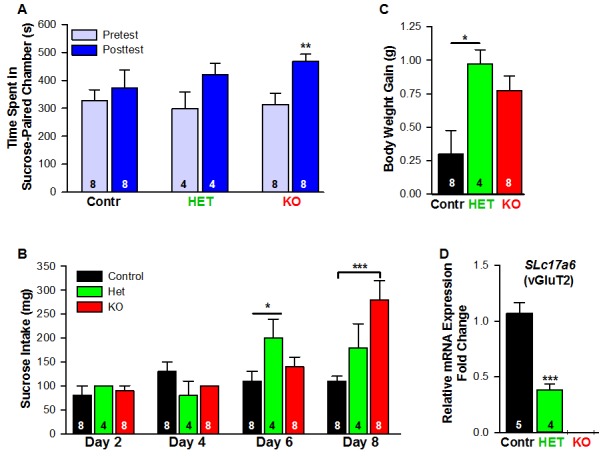
Figure 16. Female mice lacking Slc17a6 in Kiss1ARH neurons develop a conditioned place preference for sucrose.
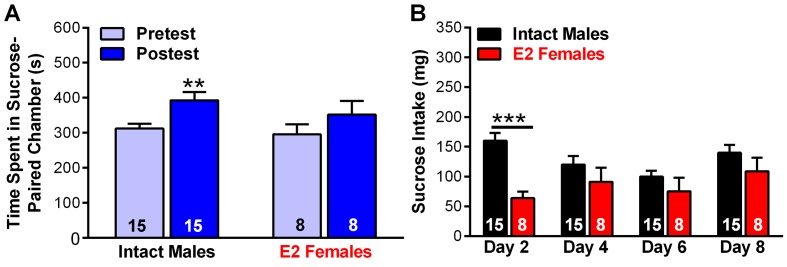
(A) Time spent in sucrose-paired chamber by control Kiss1 female mice (n = 8), Slc17a6 Het (n = 4) and Slc17a6 KO Kiss1 females (n = 8) was measured during the Pretest (Day 1, Baseline Place Preference) and the Posttest (Day 10, Conditioned Place Preference). All animals were OVX and E2-treated, and had free access to standard mouse chow in their home cage throughout the study. After sucrose conditioning, Slc17a6 KO mice developed a preference for the sucrose-paired chamber (Bonferroni post hoc test, p=0.001). Slc17a6 Het mice displayed a trend to develop a preference for the sucrose-paired chamber (Bonferroni post hoc test, p=0.086). Control Kiss1Cre female mice, however, failed to develop a preference (Bonferroni post hoc test, p=0.619). [Also, see Figure 16—figure supplement 1A for comparison between E2-treated, OVX Kiss1 female and intact Kiss1 male mice]. Two-way ANOVA: main effect of experimental group (F(2,17) = 0.298, p=0.746), main effect of protocol day (F(1,17) = 20.34, p=0.0003), and interaction (F(2,17) = 2.33, p=0.128); **p<0.01.(B) Sucrose consumption during the CPP. Sucrose intake (mg) was measured during the four sucrose-paired days (Days 2, 4, 6, and 8). Slc17a6 KO mice slightly increased their sucrose intake on Day 6 and this was significantly increased by Day 8 (Bonferroni post hoc test, p<0.0001). Slc17a6 Het mice displayed a smaller, but significant increase in sucrose intake on Day 6 (Bonferroni post hoc test, p=0.0464). [Also, see Figure 16—figure supplement 1B for comparison between E2-treated, OVX Kiss1 females and intact Kiss1 males]. Two-way ANOVA: main effect of experimental group (F(2,17) = 3.788, p=0.0436), main effect of protocol day (F(3,51) = 12.75, p<0.0001), and interaction (F(6,51) = 5.763, p<0.0001). *p<0.05, Het mice versus Kiss1 control; ***p<0.001, Slc17a6 KO mice versus Kiss1 control. (C) Body weight-gain during the ten-day CPP period. Despite that both the Slc17a6 KO and Het mice gained weight in comparison to control Kiss1 mice, only Slc17a6 Het mice were significantly different (Bonferroni post hoc test, p=0.0312, Slc17a6 Het vs Kiss1 control; p=0.066, Slc17a6 KO vs Kiss1 control;). One-way ANOVA: main effect of experimental group (F(2,17) = 5.232, p=0.017). *p<0.05, Het mice versus Kiss1 control. (D) Quantitative real time PCR measurement of Slc17a6 in Kiss1ARH neuronal pools from control Kiss1Cre:GFP mice (5 Kiss1 neurons in each pool and 5 pools from each of 5 animals) and Slc17a6 Het Kiss1 mice (5 Kiss1 neurons in each pool and 5 pools from each of 4 animals). Slc17a6 KO Kiss1 mice did not express Slc17a6 in Kiss1ARH neurons. (Unpaired t-test, t(7) = 5.791, p=0.0007). ***p<0.001, Het mice versus Kiss1 control.