Figure 6.
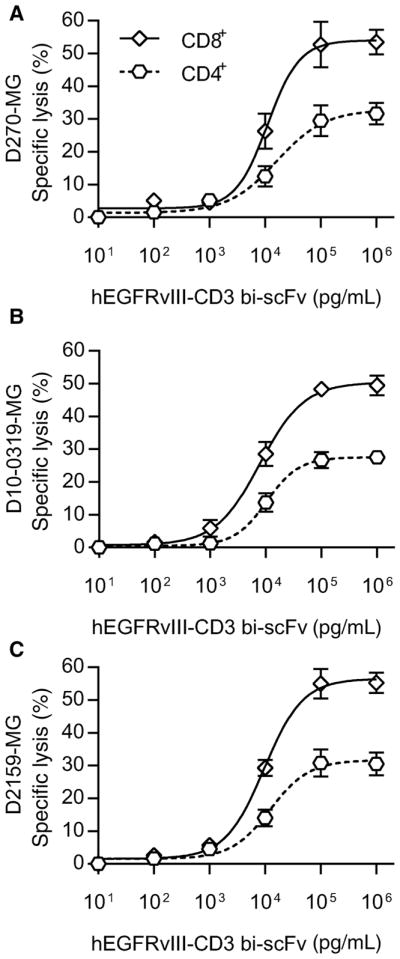
hEGFRvIII-CD3 bi-scFv redirects both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets to lyse patient-derived glioma samples. The ability of hEGFRvIII-CD3 bi-scFv to redirect both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets to independently lyse malignant glioma was assessed among three separate patient-derived glioma samples (D270-MG, D10-0319-MG, and D2159-MG). CD4+ or CD8+ T-cell subsets were isolated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and paired independently with patient-derived glioma cells at increasing concentrations of hEGFRvIII-CD3 bi-scFv. A dose-response–based increase in tumor cell lysis was observed in all cases, with both CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell subsets capable of inducing cytotoxic responses. For the D270-MG patient-derived glioma cells, at the maximum dose of hEGFRvIII-CD3 bi-scFv tested (106 pg/mL), CD8+ T cells induced significantly more cytotoxicity compared with CD4+ T cells (P = 0.0123) with the CD8+ T-cell subset inducing 53.52% ± 3.788% specific lysis compared with the CD4+ T-cell subset that induced specific lysis of 31.67% ± 3.327% of tumor cells (A). Similar trends were observed for the D10-0319-MG (B) and D2159-MG (C) patient-derived glioma cells. At a dose of 106 pg/mL of hEGFRvIII-CD3, the CD8+ T-cell subset induced a specific lysis rate of 49.50% ± 3.064% and 55.27% ± 3.138% compared with the CD4+ T-cell subset that induced a specific lysis rate of 27.55% ± 1.555% and 30.56% ± 3.464% when paired against the D10-0319-MG and D2159-MG patient-derived glioma samples, respectively. The CD8+ T-cell subset–specific lysis rate was significantly higher compared with the CD4+ T-cell subset–specific lysis rate for both D10-0319-MG and D2159-MG (P = 0.0031 and P = 0.0061, respectively). In all cases, however, the CD4+ T-cell subset induced significant cytotoxic responses (P = 0.0007; P < 0.0001; and P = 0.0009 for D270-MG, D10-0319-MG, and D2159-MG, respectively).
