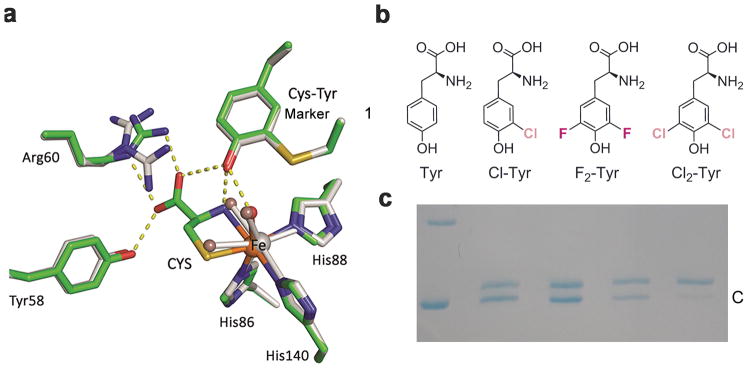
Figure 1. Crystal structures of human CDO and incorporation of unnatural amino acids into the catalytic active site tyrosine.
a, Overlay of the active site of the ligand-free (grey) and substrate (CYS)-bound complex (green) crystal structures of human CDO (PDB entries: 6BGF & 6BGM). Arg60 presents two conformations in the ligand-free structure. The omit Fo-Fc electron densities for the water ligands (WAT) and the L-cysteine are shown in Supplementary Figure 2a,b. b, Native tyrosine and halogen-substituted unnatural tyrosine analogous used in this study, i.e., L-Tyr, 3-Cl-L-Tyr (Cl-Tyr, 1), 3,5-F2-L-Tyr (F2-Tyr, 2), and 3,5-Cl2-L-Tyr (Cl2-Tyr, 3). c, SDS-PAGE shows two bands, with the slower moving band corresponding to uncrosslinked enzyme (U) and faster moving band to the mature CDO with a crosslinked cofactor (C). The lanes from left to right of the molecular weight marker are as follows: 1) wild-type CDO, 2) Cl-Tyr157 CDO, 3) F2-Tyr157 CDO, and 4) Cl2-Tyr157 CDO, respectively. The full gel image is displayed in Supplementary Figure 5b,c.