Figure 9: Model for STuBs formation and effects.
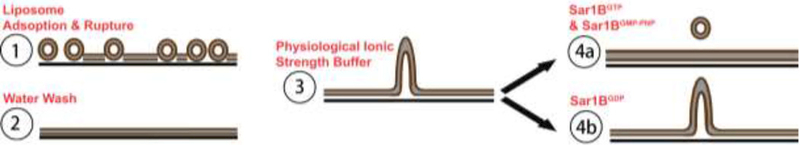
(1) SLB deposition occurs via liposome fusion. In the presence of high salt, liposomes adsorb to the glass surface faster than they rupture and spread, resulting in a bilayer containing excess lipid. (2) Washing with water removes unincorporated liposomes; although the bilayer still contains excess lipid, it appears flat for reasons that could involve decreased area per lipid and/or stronger lipid-glass interaction in water (see text). (3) Following addition of physiological ionic strength buffer, the excess lipid is no longer accommodated in the planar bilayer and tubules form. (4a-b) Effects of Sar1B addition with various nucleotides.
