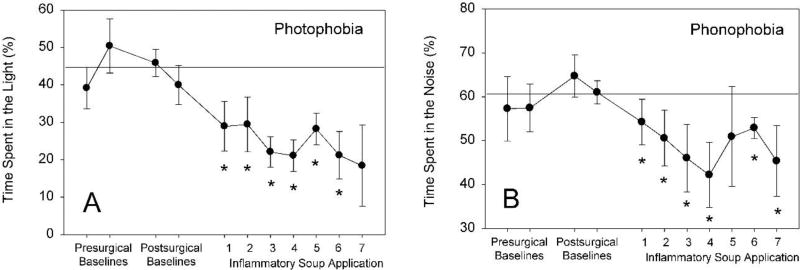
Figure 11.
Dural stimulation results in place-preference photo- and phonophobia. Baseline behaviors were assessed one and two days prior to surgery and 7 and 8 days post-surgery; the horizontal line represents the grand mean of pre- and post-surgical baseline behaviors with no dural stimulation. Dural stimulation with inflammatory soup occurred eight times over a sixteen-day period (every two or three days). Rats were introduced to the divided arena 15 minutes after inflammatory soup application, and were able to freely move in the arena for a total of 170 minutes. The first 5 min of exposure in the arena was in the absence of stimuli, the second 5 min period was in the presence of either light (250 lux), and then 5 min of noise (75 dB) present on only one side of the divided chamber, with a 2 min dark rest period between stimuli. Percentage of time in each side of the arena during the presentation of stimuli was calculated using fully automated BASi FPA Analysis software. Note subsequent applications of inflammatory soup to the dura decrease the amount of time spent in the light (A) or noisy (B) side of the chamber (* p<0.05 compared to baseline, ANOVA, Dunnett’s post-hoc; n=3–8).