Fig. 3.
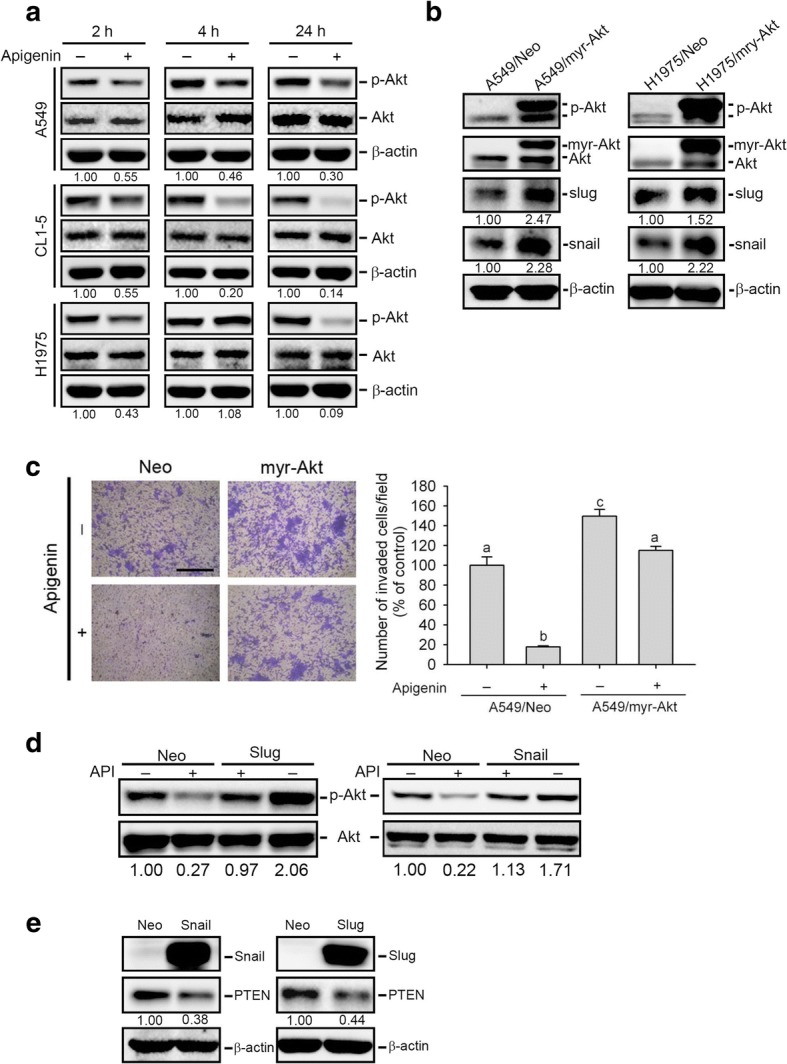
Interplay between Akt activation and Snail family expression is involved in apigenin (API)-mediated inhibition of cell motility. a Akt activation (phosphorylation) was assessed by a Western blot analysis in three non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines (A549, CL1–5, and H1975) after treatment with API (40 μM) for 2, 6, and 24 h. b, c Western blot analysis of p-Akt, Snail, and Slug expressions (b) and the invasive ability (c) of NSCLC cells (A549 and H1975) which were transiently transfected with a vector control or myr-Akt followed by API (40 μM) or vehicle treatment for an additional 24 h. Quantitative results by counting invaded cells in a 100× field. Multiples of differences are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed with a one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc tests at 95% confidence intervals; different letters represent different levels of significance. Scare bar, 500 μm. d Western blot analysis of Akt phosphorylation in A549 cells which were transiently transfected with either pLEX-Snail (A549/Snail), pCIneo-Slug (A549/Slug), or their respective controls (A549/Neo) followed by API (40 μM) or vehicle treatment for an additional 24 h. e Effect of Snail or Slug overexpression on phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) expression in A549 cells. Quantitative results of p-Akt and other indicated proteins were respectively adjusted to total Akt protein and β-actin protein levels
