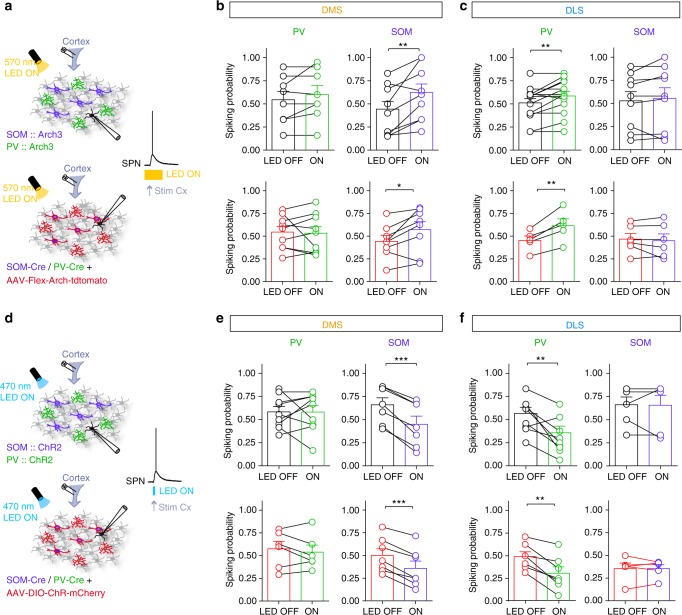
Fig. 3.
Selective modulation of cortically-evoked spiking activity by SOM and PV cells. a Experimental set up: electrical stimulations were applied in the cortex and evoked APs were recorded in SPNs, in control or with specific opto-inhibition of PV cells or SOM cells in transgenic mice PV::Arch3 and SOM::Arch3 (top) or PV-Cre and SOM-Cre mice virally infected with AAV-Flex-Arch-tdtomato (bottom) (Arch3 activation for 300 ms with a 570 nm LED). b, c The spiking probability of SPNs was compared between interleaved control and opto-inhibition conditions in DMS (b) and DLS (c) using transgenic mice (top, black) or virally infected interneurons (bottom). Individual experiments and averaged (mean ± SEM) normalized spiking probability are represented. Opto-inhibition of SOM cells leads to a significant increase in spiking probability in DMS (n = 15, p = 0.0063 for transgenic and n = 8, p = 0.033 for virus experiments) and no difference in DLS (n = 10, p = 0.2567 for transgenic and n = 6, p = 0.55479 for viruses). For PV cells, the effect is opposite, opto-inhibition of PV cells significantly increase the spiking probability in DLS (n = 16, p = 0.0288 for transgenic and n = 5, p = 0.0063 for viruses), while their opto-inhibition has no effect in DMS (n = 7, p = 0.1854 for transgenic and n = 9, p = 0.8007 for viruses). d Experimental set up: electrical stimulations were applied in the cortex and evoked APs were recorded in SPNs, in control or with specific opto-activation of PV cells or SOM cells with ChR2 activation in transgenic mice PV::ChR2 and SOM::ChR2 (top) or PV-Cre and SOM-Cre mice virally infected with AAV-Flex-ChR-mCherry (bottom) (for 5 ms using a 470 nm excitation LED). e, f The spiking probability of SPNs was compared between the control and opto-activation conditions in DMS (e) and DLS (f) using transgenic mice (top, black) or virally infected interneurons (bottom, red). Individual experiments and averaged normalized spiking probability are represented. SOM opto-activation leads to a significant decrease in spiking probability in DMS (n = 7, p = 0.0002 for transgenic mice and n = 7, p = 0.0002 for viral experiments) and no difference in DLS (n = 6, p = 0.9114 for transgenic and n = 5, p = 0.9980 for viruses). Opto-activation of PV cells significantly decrease the spiking probability in DLS (n = 9, p = 0.0059 for transgenic and n = 7, p = 0.0023 for viruses) but not in DMS (n = 9, p = 0.9816 for transgenic and n = 6, p = 0.4518 for viruses). Paired tests, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001