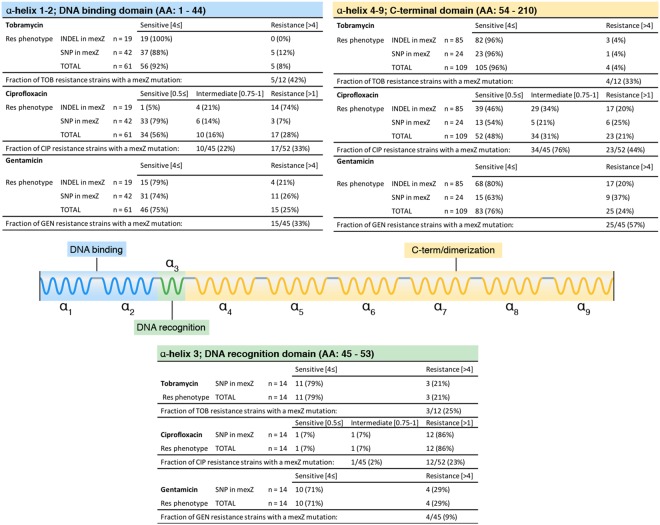
Figure 1.
Mapping of clinical obtained mutations within the mexZ gene in P. aeruginosa. Here, mexZ mutations were mapped to one of the three functional mexZ domains; the DNA binding domain (α-helix 1 to α-helix 3), where α-helix 3 is the DNA recognition helix, and a C-terminal domain (α-helix 4 to α-helix 9)19. For each domain, the number of mexZ mutations consisting of a SNP or INDEL is noted with the accompanying MIC determination for the known MexXY-OprM substrates tobramycin, ciprofloxacin, and gentamicin. The clinical break-off points are presented according to EUCAST guidelines21.