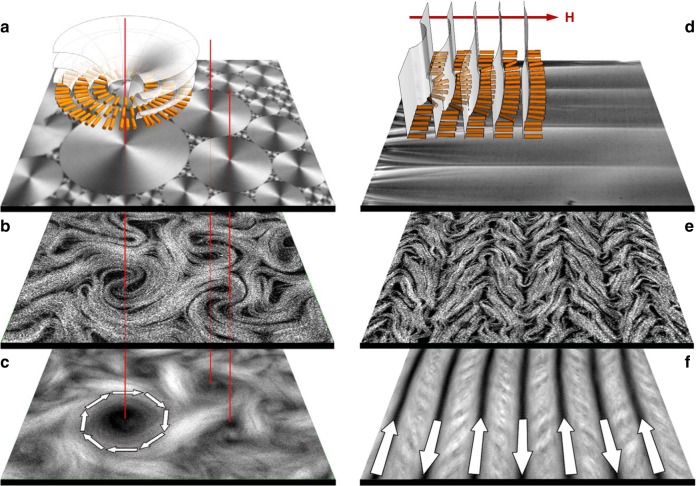
Fig. 2.
Alignment of an active nematic by anisotropic soft interfaces. In a–c the active nematic is in contact with an unconstrained smectic-A phase. In d–f, an external magnetic field (H) has aligned the smectic-A. In a and d the confocal reflection micrographs show the structure of the smectic-A phase at the interface with the aqueous phase in each case. The diagrams are sketches indicating the ordering of the smectic-A planes and liquid crystal molecules. b, e Fluorescence confocal micrographs of the active nematic layer with dynamical patterning that results from contact with the anisotropic interface. c, f Time averaged fluorescence confocal micrographs (total integration time 300 s). Arrows indicate the direction of the organised active flow. Field of view is 300 ×300 μm15,68. (Adapted with permission from Nature Publishing Group and AIP Publishing)