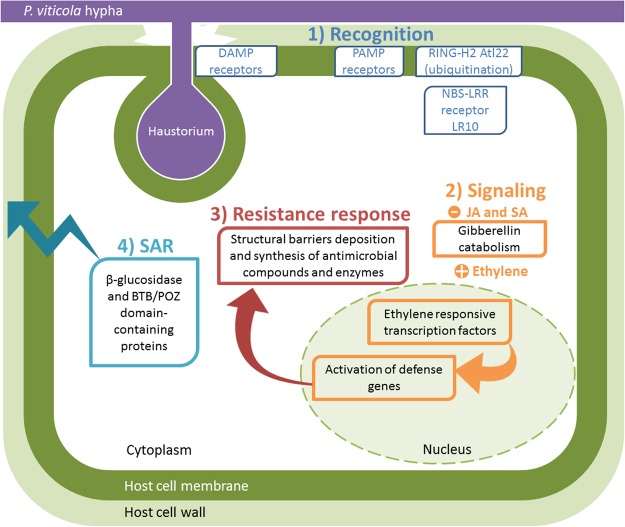
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the putative resistance mechanism of Mgaloblishvili (in green) against P. viticola (in purple) based on the overexpression of genes involved in the plant defense pathway at 1 dai. (1) Pathogen recognition through PAMP, DAMP and effector receptors, and ubiquitination. (2) Phytohormone signaling based on ethylene. (3) Resistance response based on synthesis of antimicrobial compounds and fungal wall degradating enzymes, and cell wall reinforcement. (4) Systemic signaling based on the indirect activation of the disease resistance protein PR1 that is involved in Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR).