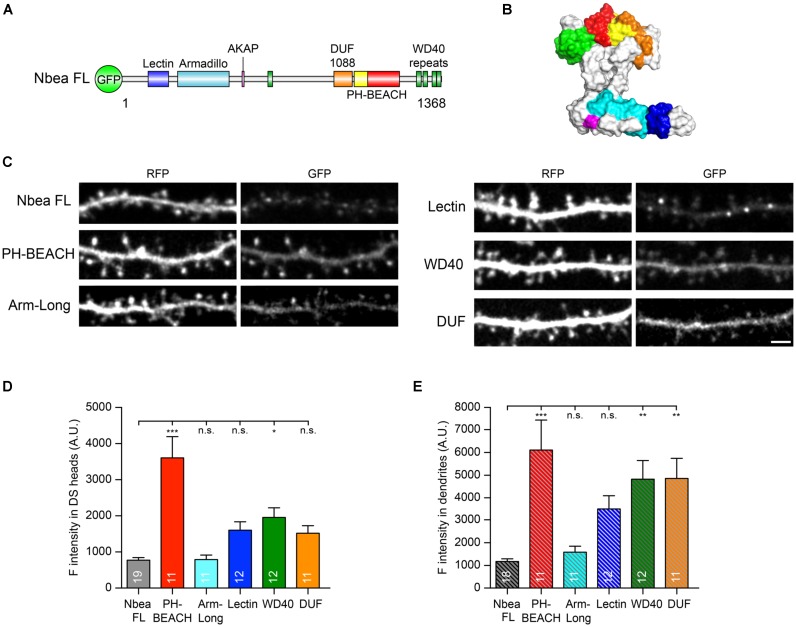
FIGURE 3.
Individual Nbea domains are able to localize to dendrites and spines. (A) Nbea motif architecture depicting its multidomain composition. GFP, N-terminally fused EGFP tag; Lectin, concanavalin A-like lectin domain; Armadillo, armadillo repeat; AKAP, A-kinase anchoring protein; DUF1088, domain-of-unknown-function; PH, pleckstrin homology-like domain; BEACH, Beige and Chediak-Higashi domain; WD40, tryptophan-aspartic acid repeats. (B) Predicted structural model of Nbea with domains color coded as in (A). See “Materials and Methods” section for details on templates and modeling procedure. (C) Representative images of dendrites from primary hippocampal neurons transfected with cytosolic marker t-dimer-RFP and isolated GFP-tagged Nbea domains as indicated. Scale bar: 2.5 μm. (D) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of individual Nbea domains in dendritic spine (DS) heads. Data are means ± SEM (arbitrary units, A.U.). N, number of neurons (in bars); quantification was carried out on at least 50 spines per neuron. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; n.s., not significant, ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. (E) Quantification of fluorescence intensity of individual Nbea domains in dendritic shaft. Data are means ± SEM (arbitrary units, A.U.). N, number of neurons (in bars); quantification was carried out on at least four 20 μm-long dendritic windows per neuron. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; n.s., not significant, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.