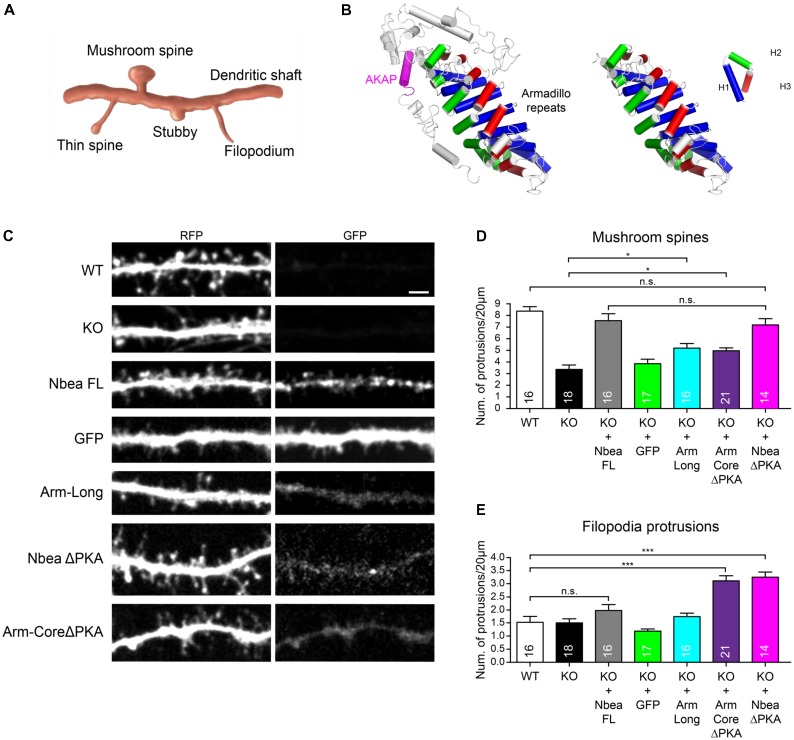
FIGURE 6.
Armadillo domain and AKAP motif of Nbea affect filopodia formation. (A) Scheme depicting major categories of DS morphology, including mature mushroom spines, long thin spines, stubby spines, and filopodia. (B) Structural model of Arm-Long sequences (left) including the AKAP helix (magenta) and Arm-Core (right). An Armadillo domain consists of eight repeats of three helices H1 (blue), H2 (green), and H3 (red). The AKAP domain of Nbea is present in the Arm-Long construct but deleted in the Arm-Core ΔPKA construct (C–E). (C) Representative dendrites of primary hippocampal neurons from wild-type (WT) and Nbea null-mutant (KO) mice transfected with cytosolic marker t-dimer-RFP alone and in combination with GFP-tagged full-length Nbea (KO + Nbea FL), Armadillo domain with AKAP motif (KO + Arm-Long), Armadillo domain without AKAP (KO + Arm-CoreΔPKA) and full-length Nbea lacking the AKAP (KO + NbeaΔPKA). As additional control, KO neurons were mock transfected with GFP alone (KO + GFP). Scale bar: 2.5 μm. (D) Quantification of number of mushroom-shaped DS in WT and Nbea KO neurons and upon expression of Nbea domains as detailed in (C). Values for WT, KO, KO + FL, and KO + GFP are the same as in Figure 4B and displayed here again to allow for easy comparison with individual domains. Data are means ± SEM, N, number of neurons (in bars). Quantification was carried out by analyzing the whole dendritic tree for each t-dimer-RFP transfected neuron. ∗P < 0.05, n.s., not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. (E) Quantification of filopodial protrusions in WT and Nbea KO neurons and upon expression of Nbea domains as detailed in (C,D). Data are means ± SEM, N, number of neurons (in bars). Quantification was carried out analyzing the whole dendritic tree for each t-dimer-RFP transfected neuron. ∗∗∗P < 0.001, n.s., not significant by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.