FIGURE 5.
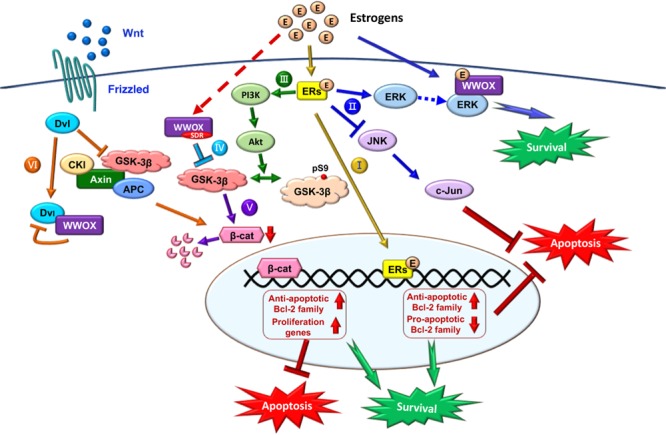
Role of E2/ER/WWOX in initiating protective pathways. The pathways include: Route I, E2/ER-mediated upregulation of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, and downregulation of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members (Yao et al., 2007) (see the route in yellow line). Route II, Activation of the pro-survival ERK/WWOX and PI3K/Akt signaling cascades to block the pro-apoptotic JNK signaling and protect the neural tissues from damages (Tang et al., 2014) (route in blue). Route III, E2 activates PI3K via ERα and mERs, followed by activating Akt to phosphorylate GSK-3β at Ser9 for functional inactivation (Ruiz-Palmero et al., 2013) (route in green). Route IV, The SDR domain of WWOX binds and limits GSK-3β activity for neuroprotection (Wang et al., 2012) (route in light blue). Route V, Suppression of GSK-3β (e.g., by WWOX) leads to a reduced β-catenin degradation, which is regulated by E2 through the ERα/PI3K/AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway (Perez-Alvarez et al., 2012) (route in purple). Route VI, In the Wnt/Frizzled signaling pathway, Wnt protein induces the activation of Dvl to block the activity of GSK-3β. Without Wnt, β-catenin is subjected to destruction by the complex of axin, APC, CK1α, and GSK-3β (Bouteille et al., 2009). Transiently overexpressed WWOX binds Dvl to suppress the Wnt signaling (Bouteille et al., 2009) (route in orange).
