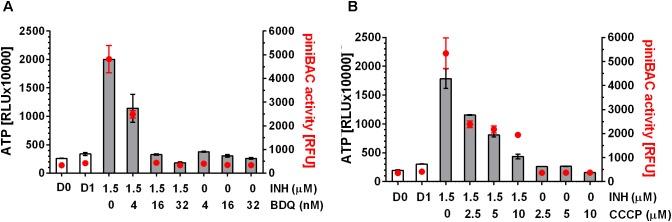
FIGURE 2.
Effect of co-treatment of M. bovis BCG piniBAC-RFP with cell wall synthesis inhibitor INH and inhibitors of oxidative phosphorylation on ATP level and piniBAC activity. (A) Exponentially growing M. bovis BCG piniBAC-RFP cultures were co-treated with the mycolic acid synthesis inhibitor INH at MIC (1.5 μM) and increasing sub-MIC concentrations of the F-ATP synthase inhibitor BDQ for 24 h (MIC BDQ = 0.26 μM). Then ATP content was measured with the BacTiter-GloTM assay (“ATP,” gray bars, in relative light units, RLU). iniBAC promoter activity was measured by determining the fluorescence of the cultures (“piniBAC activity,” red circles, in relative fluorescence units, RFU). D0 and D1 show the RLU and RFU values at the start and the end of the experiment for drug free cultures. (B) Same experiment as in (A) replacing the F-ATP-synthase inhibitor BDQ with the protonophore CCCP. MIC CCCP = 50 μM. Experiments were carried out three times independently in duplicates. Mean values and standard deviations for one representative experiment are shown. Note: the RLU and RFU numbers are not normalized for growth. As the assay time (24 h) was kept short (within one generation time) the maximum increase in OD600 (drug free) was two-fold [reflected by slight increases in RLU and RFU of drug-free samples at day 1 (D1) compared to the start of the experiment (D0)]. For all drug containing samples OD600 increased 1.5 to 2 fold.