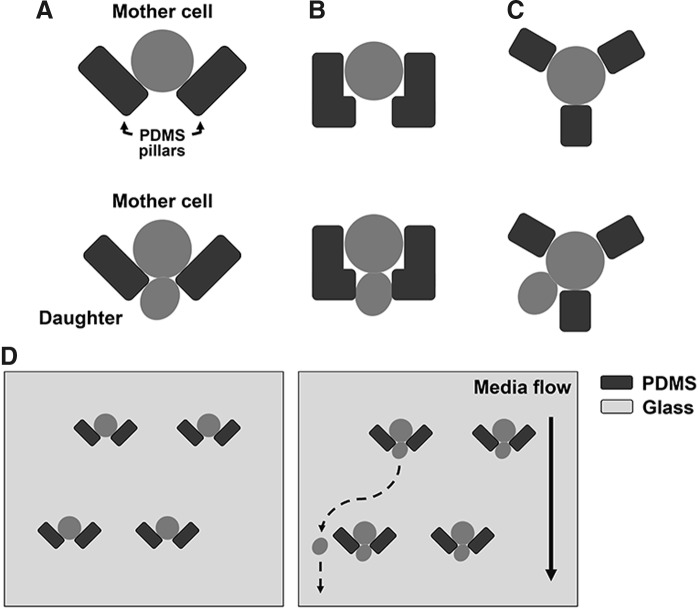
FIG. 5.
Design of microfluidics systems for automated yeast replicative lifespan analysis. (A–C) At the beginning of the experiment, mother cells are trapped by using a two-column trap in the form of V shape (A) (26), two L-shaped PDMS pillars (B) (82), or a three-column jail (C) (115, 153). (D) Smaller daughter cells are constantly removed by media flow. Yeast lifespan is monitored by counting the number of daughter cells produced by each mother cell before it undergoes senescence.