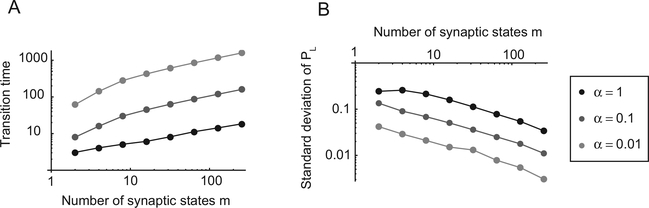
Figure 4:
Speed and accuracy as a function of m, the number of synaptic states, and of a, the learning rate (αn = αr = α, γ = 0). (A) Time τ required to converge to an estimate of the baiting probability versus m. Different curves correspond to different values of α. τ(α,Μ) is approximately . (B) Standard deviation of PL versus m for different values of α. As m increases, the fluctuations decrease approximately as , and the accuracy of the estimate increases. The initial fractional baiting probability is , and at time zero, it changes to . τ is estimated as the time it takes to reach PL = 0.5, and the standard deviation of PL is estimated at equilibrium. The other parameters are T = 0.05 and rL + rR = 0.35.