Table 1.
Properties of the Tested Fluoroalcohols and Their Nonfluorinated Counterparts
| Namea | Structureb | pKac | D (mM)d | Kpe | malcf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol |  |
15.9 | 147 ± 13 | 1.9 ± 3.3 | 0.20 |
| 2-Propanol | 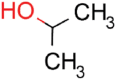 |
16.5 | 93.3 ± 5.9 | 4.9 ± 2.4 | 0.29 |
| tert-Butanol | 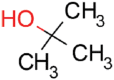 |
16.5 | 48.3 ± 4.5 | 7.9 ± 1.3 | 0.26 |
| TFE |  |
12.4 | 54.3 ± 1.8 (pH 7) | 7.2 ± 4.4 | 0.26 |
| 51.9 ± 6.8 (pH 4) | |||||
| HFIP | 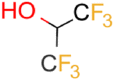 |
9.3 | 5.6 ± 0.4 (pH 7) | 66.7 ± 4.9 | 0.25 |
| 7.8 ± 1.0 (pH 4) | |||||
| PFTB | 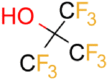 |
5.4 | 1.4 ± 0.2 (pH 7) | 878 ± 10 | 0.49 |
| 2.1 ± 0.3 (pH 4) |
Name, alcohol name.
Structures were drawn using MarvinSketch 5.0.3 from ChemAxon (Budapest, Hungary).
pKa, the logarithmic acid dissociation constant; values from (71) to (72) for the regular and fluoroalcohols, respectively.
D, the concentration ± fit error (in mM) at which the alcohols double the fluorescence quench rate at pH 7.0 (and also at pH 4.0 for the fluoroalcohols).
Kp, the alcohol bilayer/aqueous phase partition coefficients (Kp) as determined by lipid depletion in the stopped flow assay (mean ± SD).
malc, the mole-fraction of alcohol in the bilayer at D.
