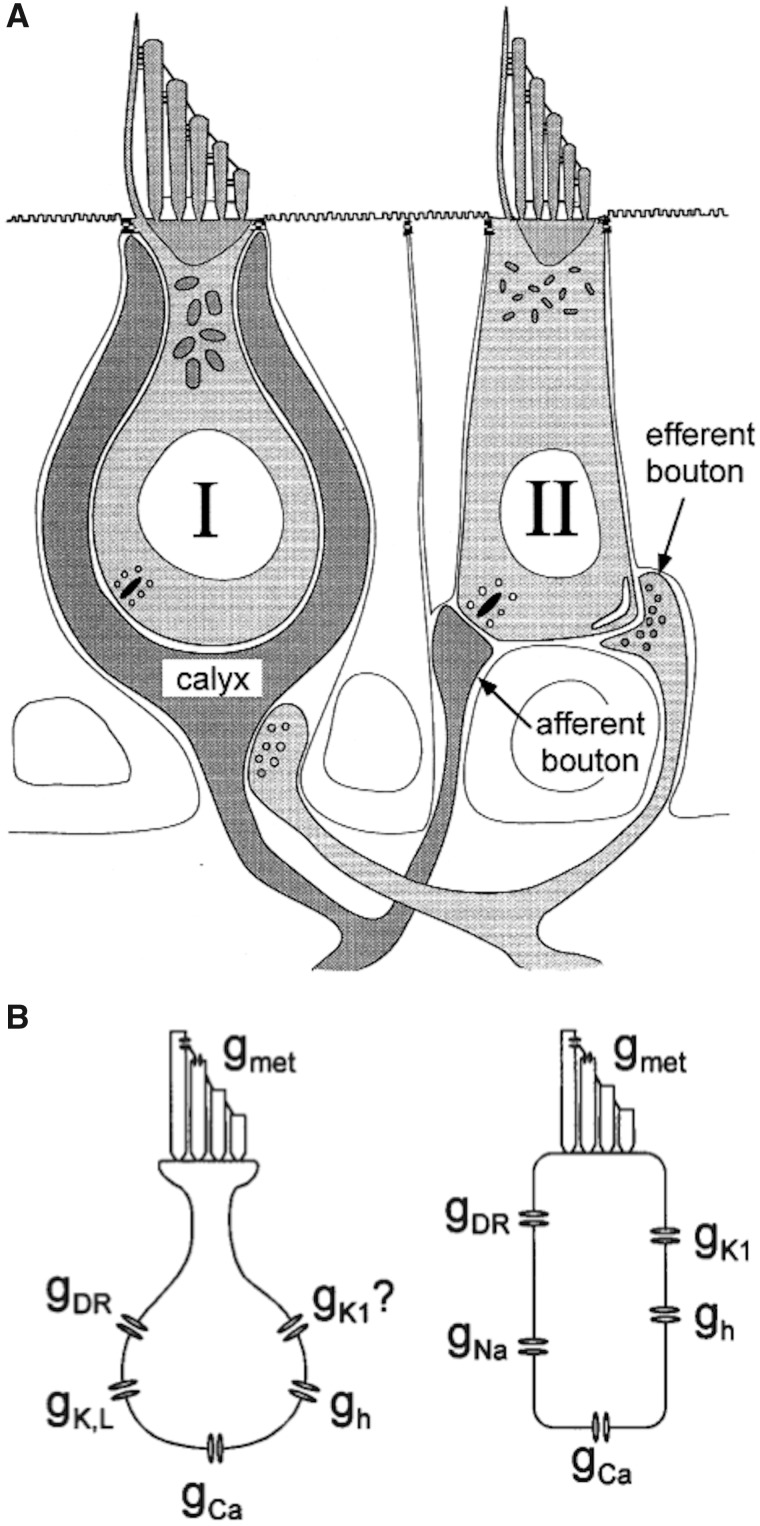
Fig. 4.
Diagram of stereotypical type I and type II hair cells from a mammalian vestibular organ. (A) Note that a single primary afferent may synapse with both a type I and a type II hair cell. A single efferent neuron may synapse onto a type I afferent ending (a postsynaptic synapse) and may synapse onto a type II hair cell (a presynaptic synapse) or onto the afferent axon (a postsynaptic synapse, not illustrated). But an efferent neuron cannot synapse onto a type I hair cell directly. (B) Ionic conductances that have been identified in vestibular hair cells. GDR, delayed rectifier K+ conductance; GK, L, K+ leak conductance; GCa, voltage-sensitive, noninactivating Ca2+ conductance; GNa, TTX-sensitive, voltage-sensitive Na+ conductance; GKI, K+- selective inward rectifier; Gh, hyperpolarization-activated inward current; GA, voltage-sensitive, rapidly inactivating K+ conductance, or A-current; GDRI, delayed rectifier K+ conductance; GDRII, delayed rectifier K+ conductance; GMET, mechanoelectrical transduction conductance. Reproduced with permission from Eatock et al. (1998).