Fig. 1.
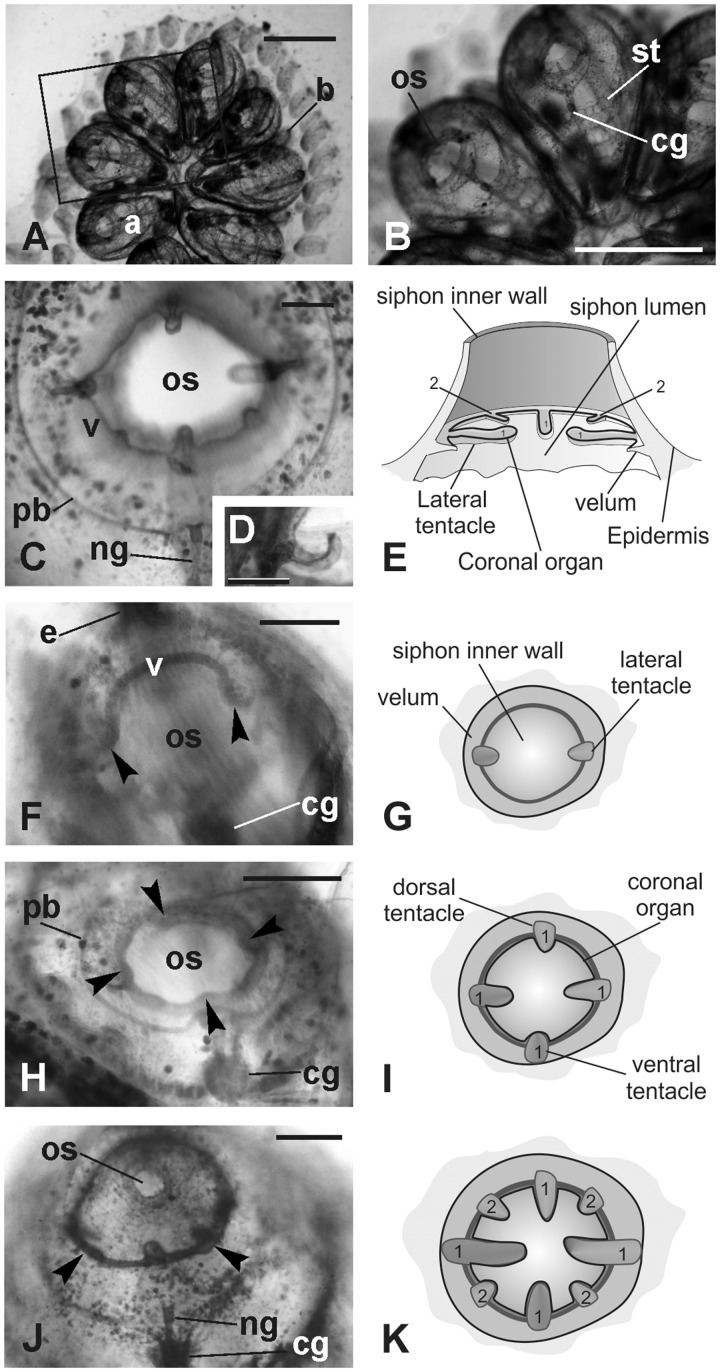
Oral siphon development. Whole mounted colonies. (A–B) Dorsal views of a colony in mid-cycle. The square area in A is enlarged in B to show the adult blastozooid organization. (C–D) Oral siphon in an adult blastozooid in mid-cycle. The four first order tentacles and two of the second order tentacles are recognizable (the other two are out of focus). A thin velum (v) joins the tentacles. Note in D that the upper surface of the tentacle is spoon shaped. (E) Schematic drawing of the oral siphon in adult blastozooid. 1, first order tentacles; 2, second order tentacles; (F–K) Tentacles and velum development in buds; oral siphons closed. F, H, and J: whole mount specimens, dorsal view. G, I, and K: sketches of oral siphon rudiment (ventral view) corresponding to the stages shown in F, H, and I, respectively (i.e., early, mid, and late cycle buds, respectively). In F, lateral tentacles (arrowheads) and velum (v) are recognizable. In H, the four first order tentacles are visible (arrowheads). In J, two of the second order tentacles (arrowheads; 2 in K) are alternated with longer ones that belong to the first order (1). a, adult blastozooid; b, bud; cg, cerebral ganglion; ng, duct of the neural gland; os, oral siphon; pb, peripharyngeal band; st, stigma. Scale bars: A and B, 1 mm, C, D, F, H, and J, 100 µm.