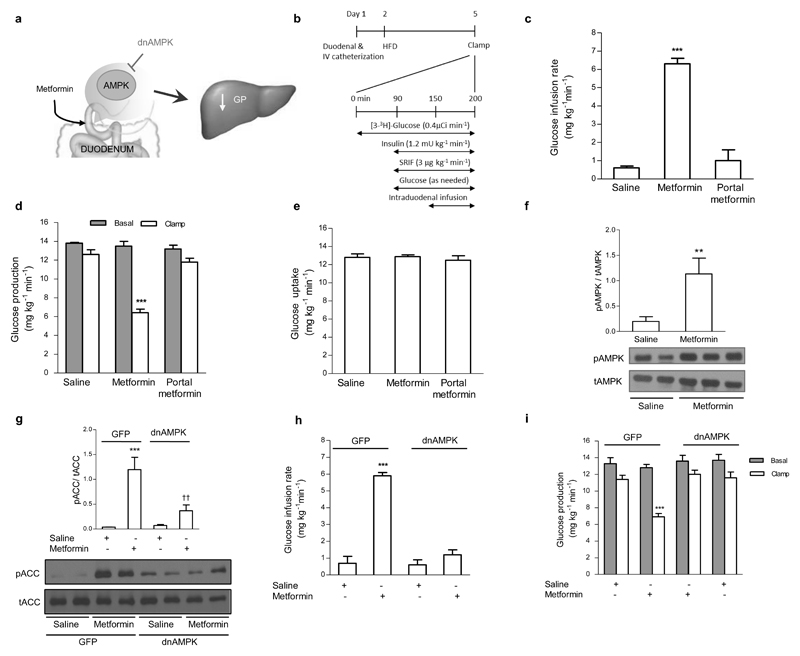
Figure 1. Intraduodenal metformin infusion activates duodenal AMPK to lower GP in the preasbsorptive state.
(a) Schematic representation of the working hypothesis. Intraduodenal preabsorptive metformin triggers duodenal AMPK to lower hepatic glucose production. (b) Experimental procedure and pancreatic (basal insulin) euglycemic clamp protocol. (c,d,e) The glucose infusion rate (c) and rate of GP (d), and rate of glucose uptake (e) during the pancreatic (basal insulin) euglycemic in HFD-fed rats with intraduodenal saline (n=7) or metformin infusions (n=6), or portal vein metformin infusion (n=5). (f) Duodenal mucosa pAMPK protein expression normalized to tAMPK in HFD-fed rats with intraduodenal saline or metformin (**p < 0.01, calculated by unpaired t-test; n=6,6). (g) pACC protein expression normalized to tACC in HEK 293 cells infected with either GFP or dnAMPK and treated with saline or metformin for 6 hours (***p < 0.001, between saline within viral group; ††p < 0.01, between viral group within treatment; as calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test; n=4 per treatment). (h,i) The glucose infusion rate (h) and rate of GP (i) during the pancreatic (basal insulin) euglycemic clamp in HFD-fed with either duodenal GFP or dnAMPK infection, infused with intraduodenal saline (n=5 each group) or metformin (n=7 each group). Values are shown as mean ± s.e.m. Unless noted, ***p < 0.001, versus all other groups as calculated by ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; GP, glucose production; HFD, high fat diet; SRIF, somatostatin, ACC, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase.