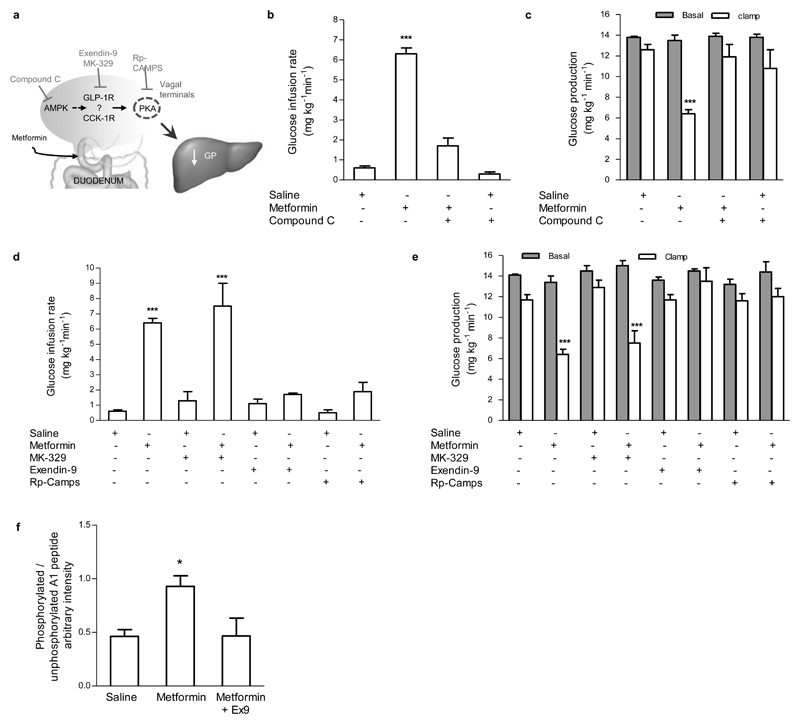
Figure 2. A duodenal AMPK – GLP-1R – PKA signaling pathway is required for metformin to lower GP.
(a) Schematic representation of the working hypothesis. Intraduodenal metformin activates duodenal AMPK, GLP-1R, and PKA to lower GP. (b,c) The glucose infusion rate (b) and rate of GP (c) during the pancreatic (basal insulin) euglycemic clamp in HFD-fed rats with intraduodenal compound C administration alone (n=5) or in combination with metformin (n=6). (d,e) The glucose infusion rate (d) and rate of GP (e) during the pancreatic (basal insulin) euglycemic clamp in HFD-fed rats with intraduodenal MK-329, exendin-9, and Rp-CAMPS administration with saline (n=5 for each) or in combination with metformin (n=6 for each group). (f) Duodenal PKA activity quantification of clamp tissue of HFD-fed rats treated with either saline, metformin, or metformin with exendin-9 (n=5 for each group). Values are shown as mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, versus all other groups, as calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; GLP-1R, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; PKA, protein kinase A; GP, glucose production; HFD, high fat diet.