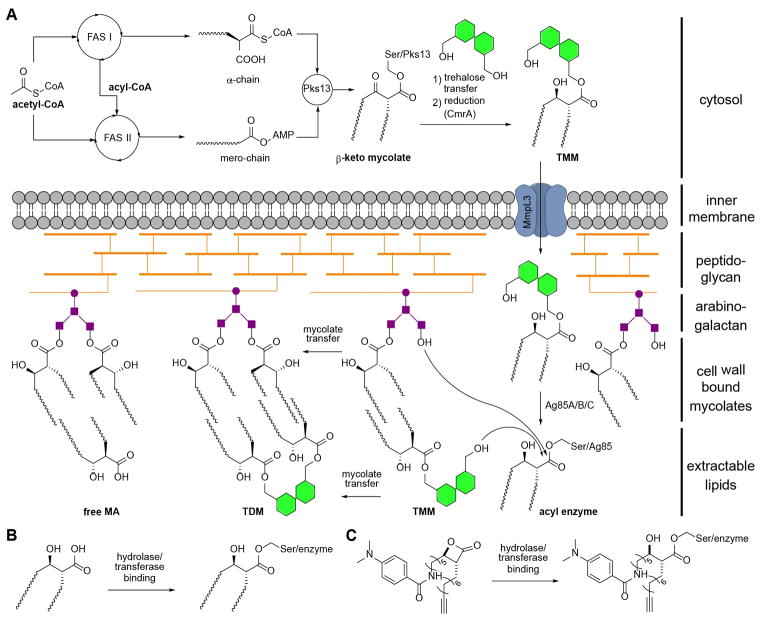
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic overview of mycolic acid biosynthesis by assembly of fatty acid chains (FAS I & II), condensation (Pks13) and maturation (CmrA) to TMM. Transfer across the inner cell membrane is receptor guided (MmpL3). Incorporation of mycolates onto the outer cell membrane is enzyme assisted (Ag85). (B) Formation of mycolic acid-hydrolase complex by acylation of active site serine. (C) Enzymatic opening of β-lactone EZ120 and acylation by active site serine. FAS: fatty acid synthase, Pks: Polyketide synthase, Ag85: Antigen 85, TMM: trehalose monomycolate, TDM: trehalose dimycolate, MA: mycolic acid, CoA: coenzyme A, AMP: adenosine monophosphate.