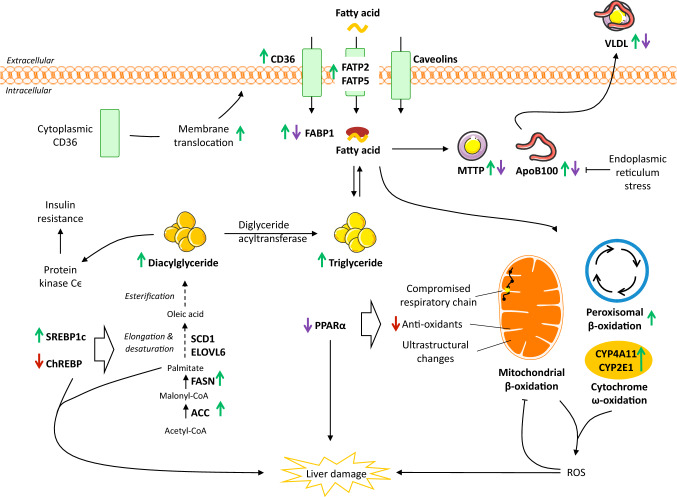
Fig. 3.
Effects on hepatic lipid metabolism in NAFLD. While the role of hepatic caveolins is still unclear, CD36, FATP2 and -5 mediates increased uptake of circulating lipids in NAFLD. Initially, FABP1 is increased, but levels may decline with disease progression, potentially limiting the mobility of fatty acids and sustaining steatosis. Enhanced SREBP1c-mediated de novo lipogenesis is a key feature of NAFLD contributing significantly to the accumulation of lipids. At the same time, ChREBP which could be hepatoprotective, appears to be downregulated in NAFLD. Although data relating to the regulation of fatty acid oxidation are conflicting, mitochondrial dysfunction is an important feature of NAFLD resulting in increased generation of ROS and utilization of cytochrome- and peroxisome-mediated oxidation. This further promotes oxidative stress, in turn inducing damage to the mitochondrial membranes, compromising cellular respiration and metabolism, and impairing liver function by direct and indirect cellular damage. Lastly, lipid export increases with hepatic triglyceride levels. However, in the setting of NASH, levels of MTTP and apoB100 may be decreased, hereby, limiting VLDL export and instead facilitating lipid accumulation. The net result is an escalating vicious circle, driven by chronic dyslipidemia and hepatic lipid overload, leading to detrimental consequences for liver metabolism and function and ultimately promoting irreversible liver damage. Green arrow: increased expression. Red arrow: decreased expression. Purple arrow: expression different between steatosis and NASH. ACC acetyl-CoA carboxylase, ApoB100 apolipoprotein B100, CD36 cluster of differentiation 36, ChREBP carbohydrate regulatory element binding protein, ELOVL elongation of very long chain fatty acid, FABP fatty acid binding protein, FASN fatty acid synthase, FATP fatty acid transport protein, MTTP microsomal triglyceride transfer protein, PPAR peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor, ROS reactive oxygen species, SCD1 stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1, SREBP1c sterol regulatory element binding protein 1c, VLDL very low density lipoprotein