Figure 7. Expression of CXorf67 reduces H3 K27-me3 in HEK293 and NSCs and eliminating CXorf67 restores H3 K27-me3 in Daoy cells.
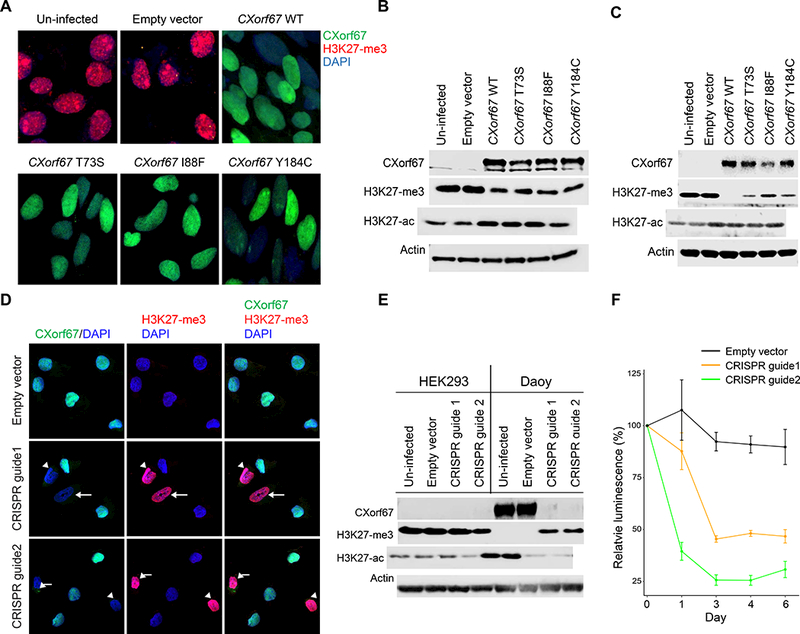
(A) Reduced H3 K27-me3 in HEK293 cells infected with a lentiviral vector expressing wildtype or mutant CXorf67. The population of infected HEK293 cells was enriched by flow sorting, and dual immunofluorescence with antibodies to CXorf67 (green) and H3 K27-me3 (red) demonstrates a reciprocal relationship between levels of these two proteins (DAPI – blue). (B) Immunoblotting of cell lysates from the experimental conditions in Figure 7A. A reduction of H3 K27-me3 follows expression of wildtype or mutant CXorf67. An increase in H3 K27-acetylation (H3 K27-ac) is evident following CXorf67 expression. (C) Immunoblotting showing similar results in neural stem cells infected with wildtype or mutant CXorf67. A reduction of H3 K27-me3 follows expression of wildtype or mutant CXorf67 and a slight increase in H3 K27-ac is evident following CXorf67 expression. (D) Daoy cells carrying vector with or without CRISPR guide 1 or 2. With an empty vector, Daoy cells express CXorf67, but not H3 K27-me3. Introduction of either CRISPR guide into some cells produces combined lack of CXorf67 expression and elevated H3 K27-me3 expression (arrows). (E) In Daoy cells flow-sorted to contain only those infected with vector, immunoblotting confirms knock-out of CXorf67 in those containing either CRISPR guide. Concomitantly, H3 K27-me3 expression is restored, while H3 K27-ac is reduced. HEK293 cells are included as a control (composite image from blots run in parallel). Elimination of CXorf67 expression reduced the growth of Daoy cells by more than half, as illustrated by a change in relative luminescence (F).
