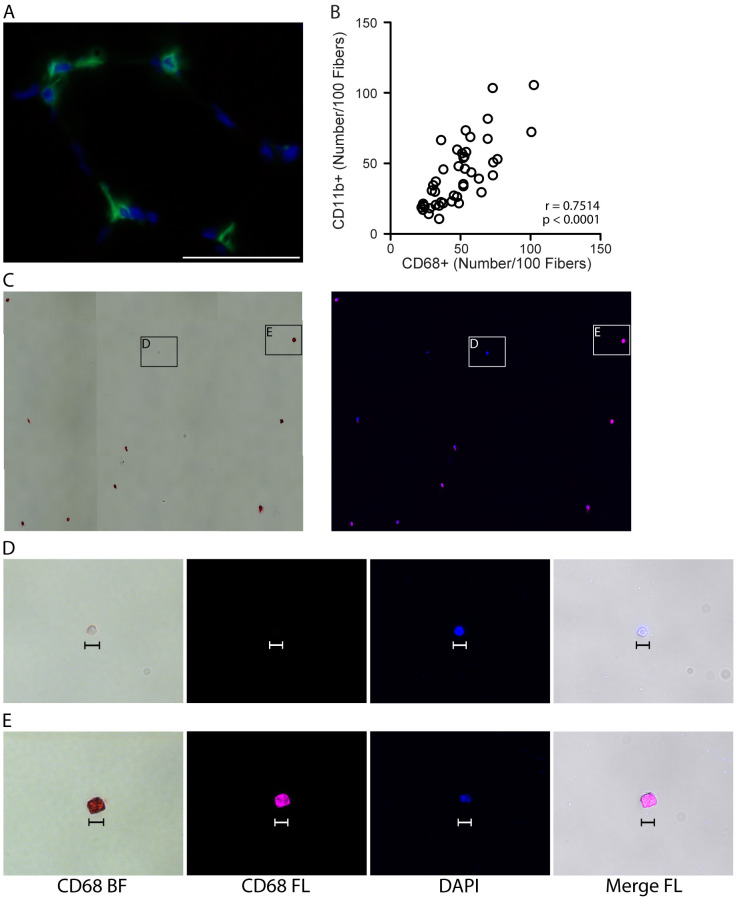
Figure 2. Validating CD11b as a pan-macrophage, cell surface marker in human skeletal muscle.
A. Representative image showing IHC for the pan, intracellular macrophage marker, CD68 (green), with DAPI stained cell nuclei (blue) in human vastus lateralis muscle. Scale bar = 50 µm. B. Correlation of CD11b+ and CD68+ macrophage numbers, identified by IHC on consecutive sections from vastus lateralis muscle, n = 44 muscle samples analyzed. P value determined by Pearson’s correlation, r = Pearson’s correlation coefficient. C. CD14+/CD11b+ mononuclear cells (shown in Figure 1, panel A) were isolated by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and stained for CD68. Positive staining is both chromogenic (red when imaged with transmitted light, bright field, BF) and fluorescent (pseudocolored pink, FL). Left image: CD68 BF; positive staining is red. Right: CD68 FL, positive staining is pink. Cell nuclei were labeled with DAPI (blue). D-E. High magnification images showing a CD68- event (D) and CD68+ cell (E) from panel C. CD68- events were small (< 10 µm) and did not appear to be monocytes/macrophages. CD68- structures appeared to stain with DAPI, suggesting that this may be cellular debris (cell nucleus without cytoplasm). Scale bars = 10 µm.