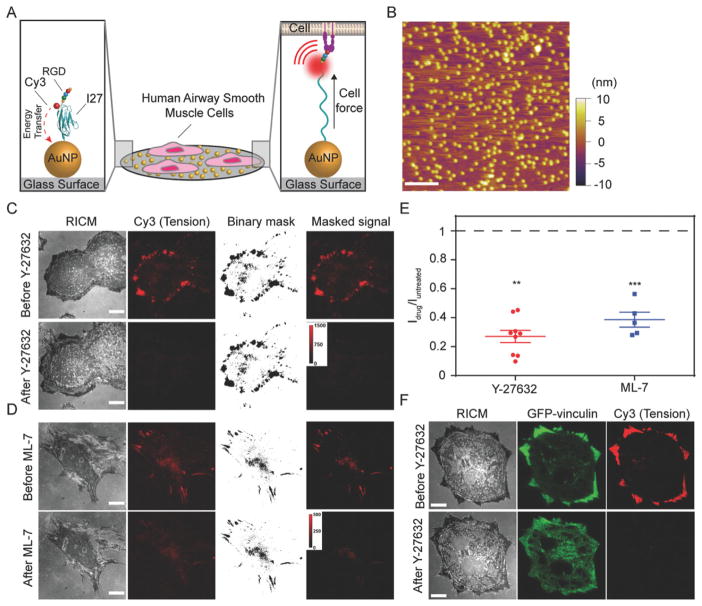
Figure 1.
Measuring airway smooth muscle (ASM) cell integrin forces using titin-based molecular tension probes. A) Schematic illustration of the RGD-Cy3-I27 MTFM sensor and its mechanism of reporting integrin forces. B) Representative AFM image of 9 nm AuNPs immobilized on a PEGylated [5% (w/v) mPEG-NHS and 0.5% (w/v) lipoic acid-PEG-NHS] glass substrate. Scale bar, 200 nm. C–D) Representative RICM and fluorescence images of human ASM cells on the tension sensing substrate before and after treatment with ROCK kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (40 μM) or ML-7 (40 μM) for 30 min. Scale bar, 10 μm. E) Plot shows the normalized tension signal, defined as Idrug/Iuntreated, of the same cells (same ROI) before and after ROCK inhibitor and ML-7 treatment. Masks were created to isolate tension signal from background. Lines represent mean±SEM from n = 9 cells for Y-27632, and n = 5 cells for ML-7 treatment from three independent surface preparations, **P <0.01 (Y-27632) and ***P < 0.001 (ML-7) by Wilcoxon signed-rank test. F) Representative RICM and fluorescence images of human ASM cells transfected with GFP-vinculin incubated on the tension sensor before and after treatment with ROCK kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (40 μM) for 3 min. Scale bar, 10 μm.