Figure 2.
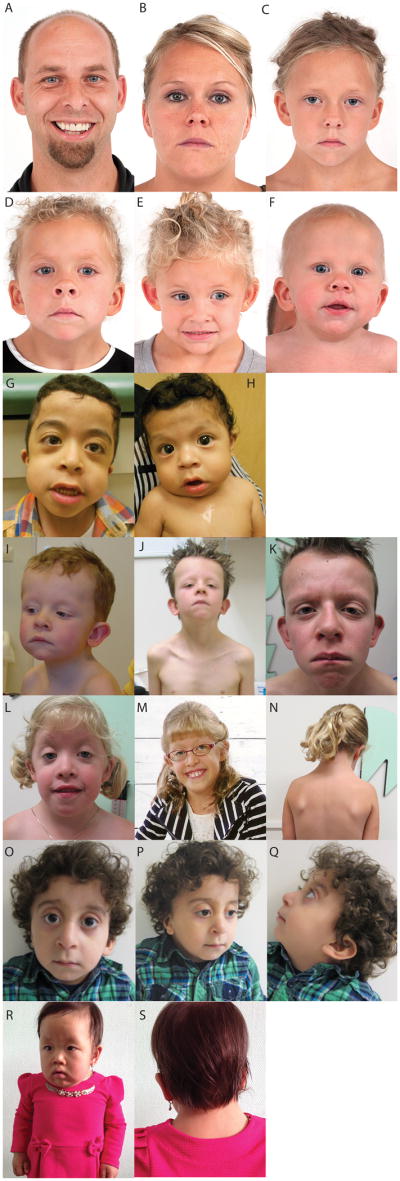
Facial features of Family 1 including unaffected parents (A, B) and four affected children (C-F). In the children note variable features of short or upturned nose, depressed bridge, low-set, posteriorly angulated, or malformed ears, midface retrusion, broad/short neck, low posterior hairline, and curly hair. Facial features of the affected brothers from Family 2 (G, H) demonstrating widely-spaced eyes, downslanted palpebral fissures, midface retrusion, full cheeks, a long philtrum, and overfolded, posteriorly angulated ears. Features of individual II-1 from Family 4 at three ages. At three years of age (I), at 7 years of age (J), and 14 years of age (K). Notice the short, broad neck, widely-spaced eyes with downslanted palpebral fissures and bilateral ptosis, low set and posteriorly angulated ears, and pectus excavatum. Affected individual from Family 5 at 4 years of age (L), 8 years of age (M) and 6 years of age (N). Her features included downslanted palpebral fissures, bilateral epicanthus and ptosis, broad neck, low-set, small, cupped ears, and a wide thorax. Affected individual from Family 8 showing widely-spaced eyes, downslanted palpebral fissures, mild ptosis, low-set and posteriorly angulated ears, a broad, webbed neck, and curly hair (O-Q). Features of individual II-2 from Family 9. Note her widely set eyes, strabismus, bilateral epicanthus, downslanted palpebral fissures, depressed nasal bridge, short and upturned nose, short and broad neck, thickened vermilion of the lips (R,S).
