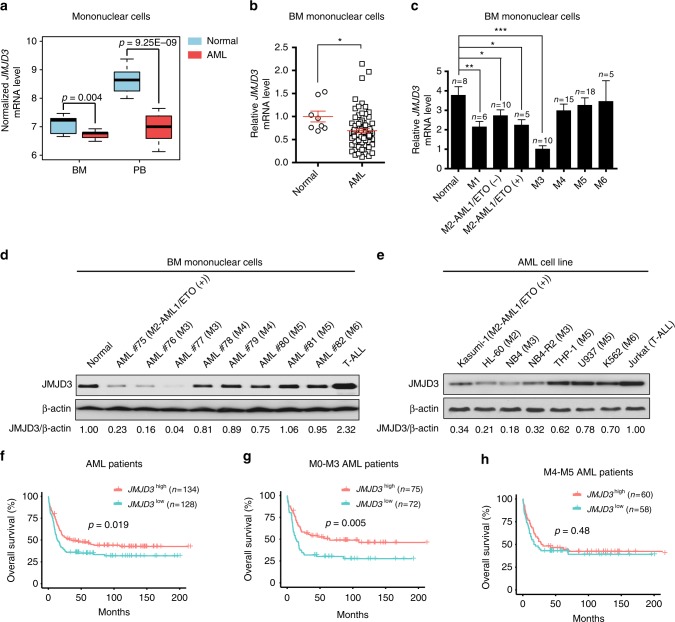
Fig. 1.
JMJD3 expressional reduction is correlated with poor prognosis in certain subtypes of AML cases. a JMJD3 mRNA levels in BM and PB mononuclear cells of AML patients (including seven BM or 19 PB samples) and in normal counterparts (ten BM and ten PB samples) were compared (raw data retrieved from GEO (GSE9476) dataset). Boxes denote interquartile range, with a line at the median, while whiskers are indicating minimal and maximal observations for each parameter. b qRT-PCR assay on the JMJD3 mRNA level in the AML blasts-enriched primary BM mononuclear cells (n = 74) or normal BM mononuclear cells (n = 8). c qRT-PCR assay on the JMJD3 mRNA level in the AML blasts-enriched primary BM mononuclear cells including subtype M1 (n = 6), M2-AML1/ETO (−) (n = 10), M2-AML1/ETO (+) (n = 5), M3 (n = 10), M4 (n = 15), M5 (n = 18), M6 (n = 5) or normal BM mononuclear cells (n = 8). d Western blotting assay on JMJD3 protein levels of eight AML blasts-enriched primary BM mononuclear cell samples, a normal BM mononuclear cell sample, and a T-ALL blasts-enriched BM mononuclear cell sample. β-actin level was used as the loading control. e Western blotting assay on JMJD3 protein levels of the established leukemia cell lines. f–h Overall survival of AML patient cohort (f), M0, M1, M2, and M3 AML patient cohort (g), or M4 and M5 AML patient cohort (h) with regard to JMJD3 mRNA levels. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001