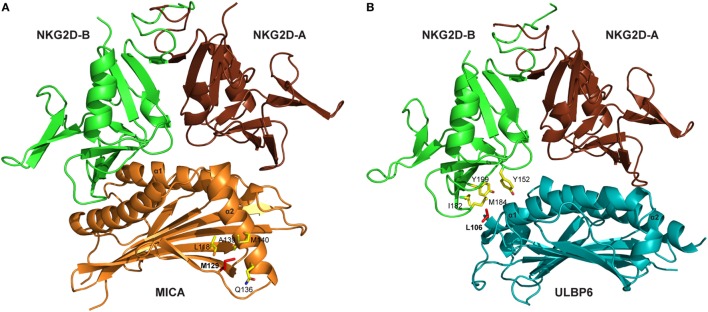
Figure 1.
Crystal structures of NKG2D-ligand complexes. (A) Ribbon representation of the MICA–NKG2D complex [PDB code 1HYR, Li et al. (10)]. NKG2D homodimer [NKG2D-A (brown) and NKG2D-B (green)] interacts with the α1 and α2 domains of monomeric MICA (orange). The clinically relevant polymorphic residue Met129 (red) in MICA is located distal to the MICA–NKG2D interface. Partially buried Met129 mediates non-polar interactions with MICA residues (ball and stick format) that protrude from the α2 helix. The α3 domain of MICA (residues Thr181-Ser274) has been omitted. (B) Ribbon representation of the ULBP6–NKG2D complex [PDB code 4S0U; Zuo et al. (13)]. NKG2D homodimer [NKG2D-A (brown) and NKG2D-B (green)] interacts with the α1 and α2 domains of ULBP6 (teal). The disease-associated polymorphic residue Leu106 (red) in ULBP0602 is in close proximity to the ULBP6–NKG2D docking interface, inserting directly into the NKG2D hydrophobic pocket lined by several non-polar residues (ball and stick format). The figure was generated with PyMOL (Molecular Graphics System, Version 2.0 Schrödinger, LLC).