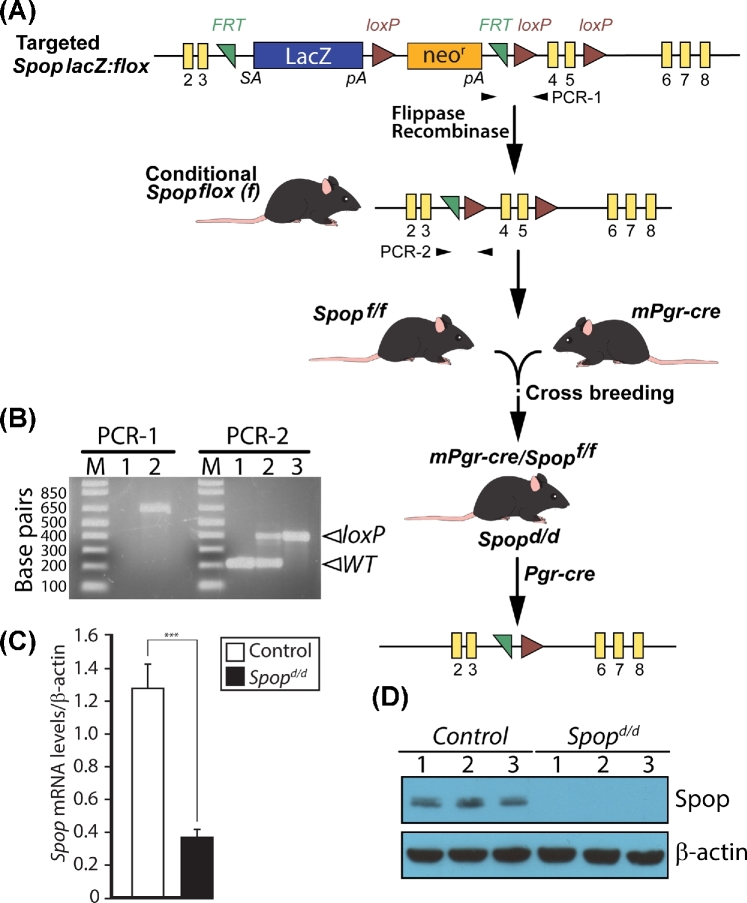
Figure 1.
Generation of the Spopd/d mouse. (A) Obtained from KOMP [13], mice carrying the Spop lacZ: flox allele were crossed with ROSA flippase mice to generate mice harboring the conditional Spop floxed allele (Spopf/f) in which exons 4 and 5 are flanked by loxP sites. The Spopf/f and mPgr-cre mouse (both C57BL6) were crossed to generate the bigenic Spopd/d mouse. Driven by the Pgr promoter, the cre recombinase excises exons 4 and 5 of the Spop gene in the Spopd/d mouse; exons 4 and 5 encode the essential MATH domain of SPOP [13]. (B) Typical PCR results are shown for genotyping mice carrying the targeted Spop lacZ: flox allele and the Spopf/f allele using the PCR-1 and PCR-2 reaction primers respectively. For the PCR-1 reaction, lanes 1 and 2 represent genotype results using tail tip genomic DNA from control mice and mice heterozygous for the Spop lacZ: flox allele, respectively; the positive PCR amplicon is 659 bp. For the PCR-2 reaction, lanes 1, 2, and 3 denote control, Spopf/+ (heterozygous for the Spop floxed allele) and Spopf/f (homozygous for Spop floxed allele) respectively; PCR-positive amplicon is 179 bp for WT allele and 397 bp for Spop floxed allele. Primer sequences for PCR-1 and -2 are listed in Materials and methods section. (C) Real-time PCR analysis clearly demonstrates a significant reduction in Spop transcript levels in the uterus of Spopd/d mice (n = 9) as compared to controls (n = 6). (D) Western analysis of protein isolated from control and Spopd/d uteri confirms that SPOP protein is not detected in the Spopd/d uterus; each lane represents a protein sample pooled from four individual adult mice per genotype (β-actin serves as a loading control).