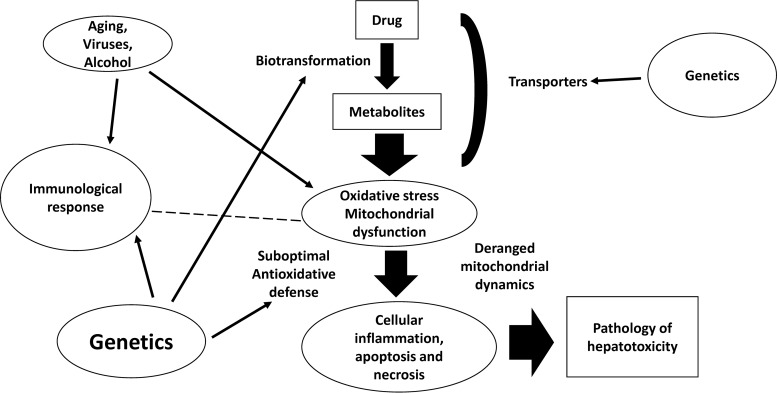
FIG 1.
A simplified representation of the pathogenesis of drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction are important mechanisms contributing to drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Genetic polymorphisms associated with drug metabolism, oxidative stress, and immune response interact in an intricate way, with conditions/diseases associated with oxidative stress per se, leading to cellular inflammation, apoptosis, and necrosis, which manifest as histopathological changes of hepatotoxicity. The dashed line indicates possible interaction between immunological response and oxidative stress.