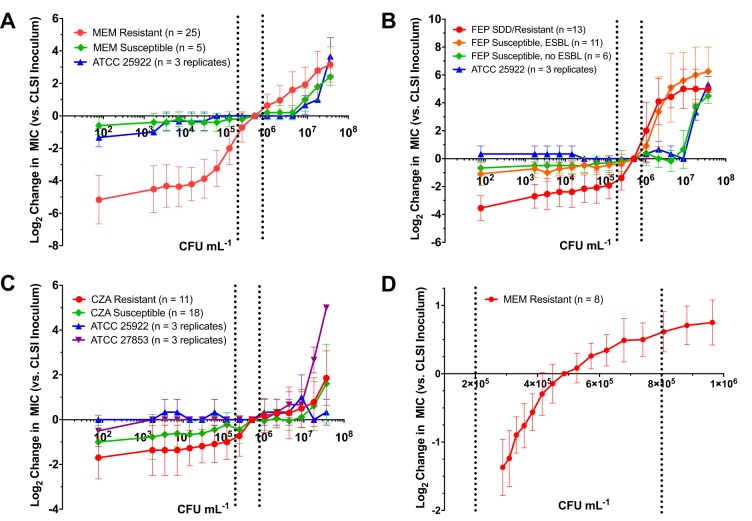
FIG 2.
Extended-range and high-resolution quantification of the inoculum effect. (A to C) Bacteria and antibiotics meropenem (A), cefepime (B), and ceftazidime-avibactam (C) were dispensed in orthogonal 2-fold dilution series. Each data point represents the log2 difference between the MIC at the indicated inoculum and the corresponding MIC at the CLSI target inoculum averaged across all strains within each category indicated. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation from the mean. Dotted lines demarcate the CLSI-recommended inoculum range. Carbapenem-resistant strains showed a pronounced reduction in meropenem MIC at inocula below the CLSI-recommended inoculum. Cefepime-resistant and -susceptible dose-dependent (SDD) strains showed a rapid increase in cefepime MIC at inocula above the CLSI-recommended inoculum. In contrast, a pronounced inoculum effect was not observed for ceftazidime-avibactam. (D) Bacteria and meropenem were dispensed using inkjet technology in (≈1.10-fold) and (≈1.19-fold) orthogonal dilution series, respectively. Each data point represents the log2 difference between the MIC determined at the indicated inoculum and the MIC at the CLSI target inoculum averaged across triplicate experiments performed on separate days using 8 CRE strains. Dotted lines demarcate the CLSI-recommended inoculum range.