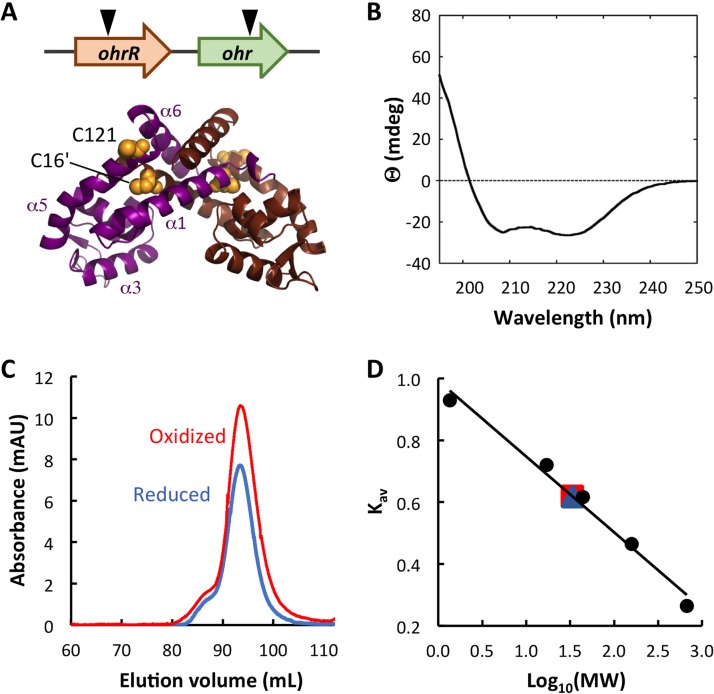
FIG 1.
B. thailandensis OhrR is a dimer. (A) (Top) The genomic locus encoding ohr and ohrR. The inverted triangles indicate the positions of transposon insertion. (Bottom) The model is based on the structure of reduced X. campestris OhrR-C22S (PDB accession number 2PEX [19]; global model quality estimate [GMQE] = 0.72). One subunit is in magenta with helices identified, and the other is in brown. Cysteine residues are in yellow space-filling representation, with C16′ in α1′ (brown subunit) and C121 in α5 (magenta subunit) being identified. The illustration was generated with the PyMOL program. (B) Far-UV CD spectrum reflecting the expected secondary structure composition. Ellipticity (θ) is reported in millidegrees (mdeg). (C) Elution of reduced and oxidized OhrR from SEC column. mAU, milli-absorbance units. (D) Standard curve reflecting MW standards eluting from the SEC column. Both reduced (blue) and oxidized (red) OhrR eluted corresponding to an MW of ∼34 kDa.