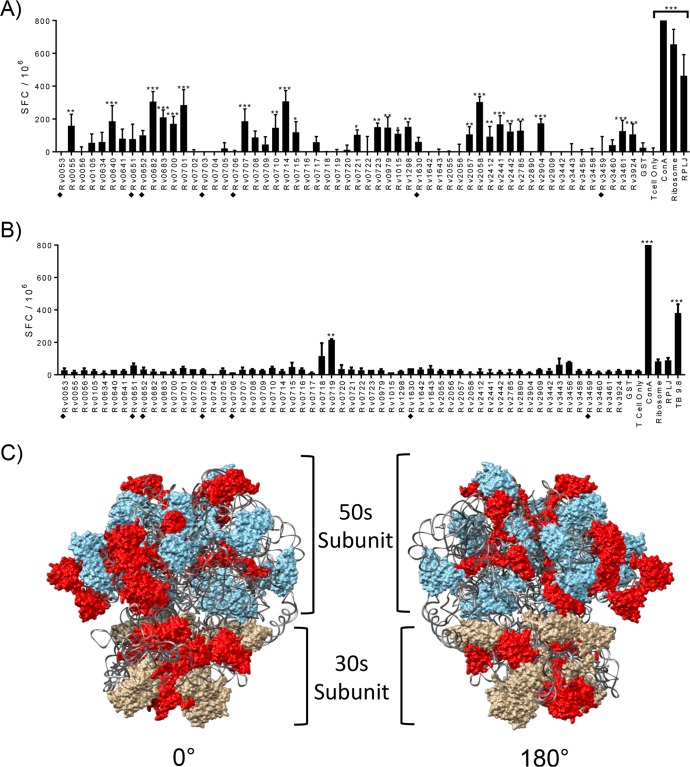
FIG 1.
Identification of M. tuberculosis ribosomal proteins recognized by CD4+ T cells from IKEPLUS- and BCG-immunized animals. (A and B) Mice (C57BL/6) (n = 3) were immunized with 5 × 107 CFU IKEPLUS i.v. (A) or 5 × 106 CFU BCG-Danish s.c. (B). Two weeks later, CD4+ T cells were purified from splenocytes and tested by an ELISPOT assay for IFN-γ production in response to ex vivo stimulation with purified recombinant preparations of each of the 57 M. tuberculosis ribosomal proteins (10 μg/ml). Responses that are significantly different from those with the negative-control stimulation with purified glutathione S-transferase (GST) by two-way ANOVA with FDR correction and a 1% cutoff are indicated (*, q < 0.01; **, q < 0.001; ***, q < 0.0001). Positive-control wells were stimulated with concanavalin A (ConA) (5 μg/ml). Additional positive controls were purified M. smegmatis ribosomes (Ribosome) (5 nM) or RplJTB146–160 peptide (RPLJ) (10 μg/ml) (A) and TB9.8 (10 μg/ml) (B). Proteins that were poorly expressed and of lower purity in our system (i.e., potential false negatives) are marked with filled diamonds. Data shown are representative of results from two independent experiments and are displayed as mean numbers of spot-forming cells (SFC) per well, with error bars representing standard errors for quadruplicate (A) and duplicate (B) samples. (C) Proteins that achieved statistical significance for stimulation of CD4+ T cell responses in IKEPLUS-immunized mice in panel A were mapped in red onto the reported structure of the mycobacterial ribosome (PDB accession number 5O61) (28). The 50S subunit is shown in blue, the 30S subunit is in tan, and the rRNA is in gray.