FIG 1.
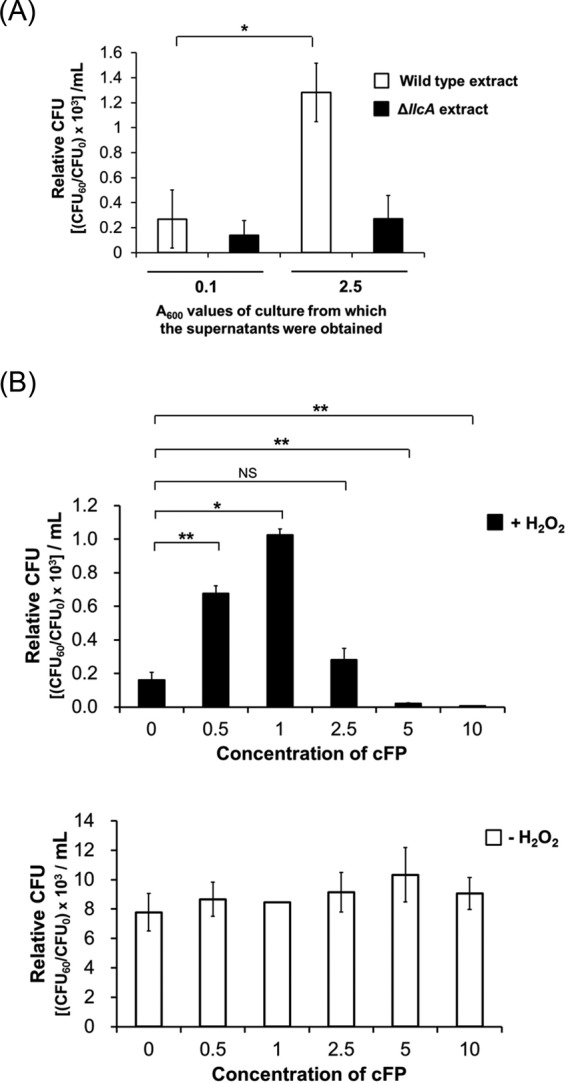
Effect of cFP on survival of V. vulnificus under H2O2-induced oxidative stress conditions. (A) Culture supernatant from wild-type V. vulnificus cells at stationary phase contributes to survival of V. vulnificus under oxidative stress. Wild-type V. vulnificus cells were treated with an ethyl acetate extract of supernatant from wild-type V. vulnificus or ΔllcA isotype cultures grown in LB broth to exponential phase (A600 = 0.1) or stationary phase (A600 = 2.5), and 625 μM H2O2 was added to each sample. Survival of cells was assessed by measuring CFU. (B) cFP at 1 mM increases survivability of V. vulnificus under H2O2-induced oxidative stress. Wild-type V. vulnificus cells grown in the presence of different concentrations of cFP were treated with 625 μM H2O2 (solid bars) or no H2O2 treatment (open bars). Cell survival was then assessed by measuring CFU. CFU were expressed as the CFU60/CFU0 ratio. CFU0 and CFU60 are CFU per milliliter at 0 min and at 60 min, respectively, after treatment or not with H2O2. The error bars denote standard deviations of the results of three independent experiments (**, P < 0.005; *, P < 0.05; NS, not significant).
