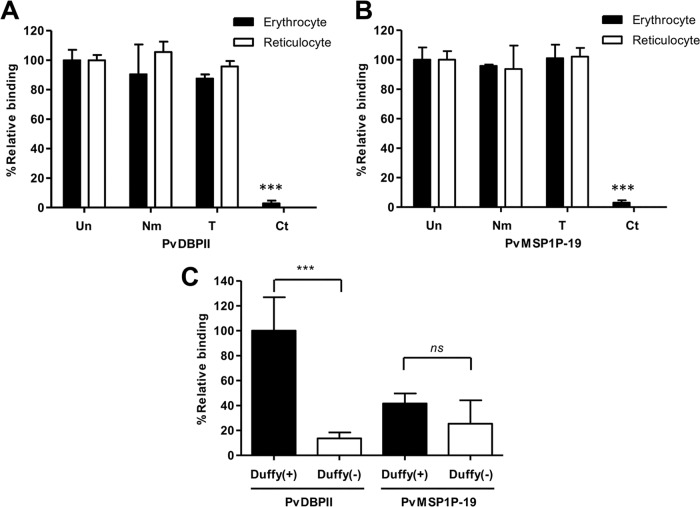
FIG 5.
Reticulocyte-specific receptors for PvMSP1P-19 binding. (A and B) PvDBPII (A) and PvMSP1P-19 (B) binding assays were performed using enzyme-treated erythrocytes and reticulocytes. Untreated (Un) erythrocytes and reticulocytes and erythrocytes and reticulocytes treated with neuraminidase (Nm), trypsin (T), or chymotrypsin (Ct) were used to confirm receptor specificity. The data are shown as the mean ± SD of the binding inhibition rate measured in three independent experiments. Significant differences compared to the results with untreated erythrocytes or reticulocytes after the enzymatic treatment of erythrocytes and reticulocytes were calculated using Student's t test and are denoted by triple asterisks (P < 0.001). (C) Binding specificity of PvMSP1P-19 and PvDBPII to Duffy-positive and Duffy-negative erythrocytes. The relative binding of PvMSP1P-19 to Duffy-positive and Duffy-negative erythrocytes was normalized to that of PvDBPII binding to Duffy-positive erythrocytes as a standard (100%). The data are shown as the mean ± SD of the relative binding measured in four independent experiments. Significant differences between Duffy-positive and Duffy-negative erythrocytes in PvDBPII and PvMSP1P-19, respectively, were observed. P values were calculated using Student's t test; significant differences are indicated by triple asterisks (P < 0.001). ns, not significant.