FIG 1 .
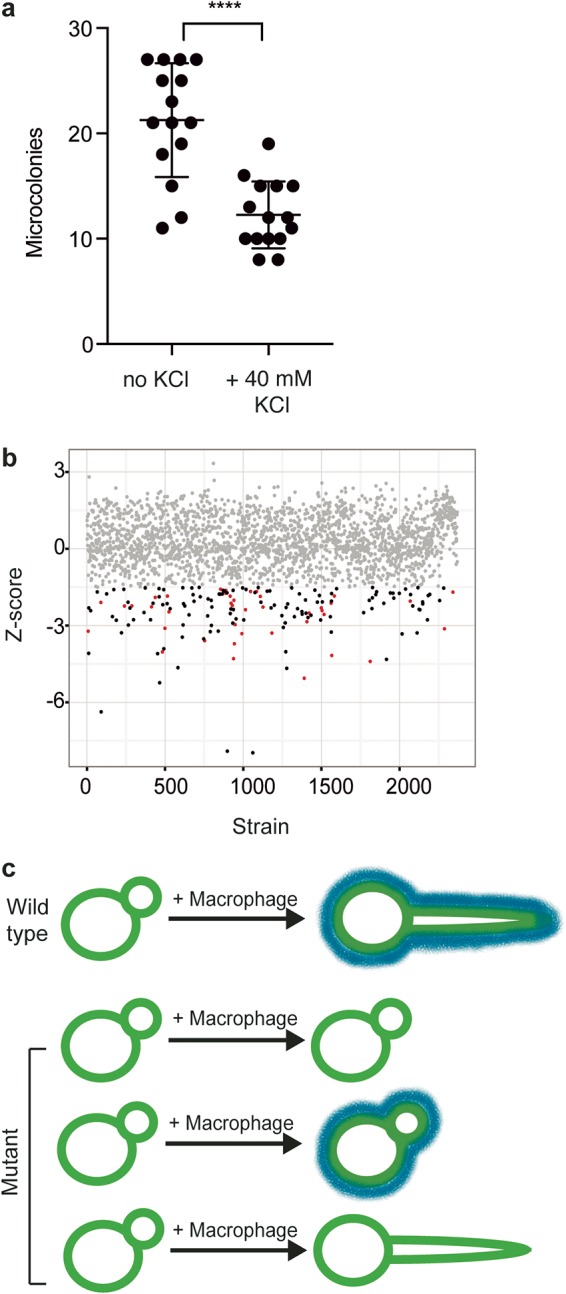
High-throughput screening to examine C. albicans-macrophage interactions. (a) Macrophage pyroptosis increases fungal survival. Macrophages were incubated with diluted C. albicans cells in the presence or absence of 40 mM KCl for 24 h. Microcolonies were counted from two biological replicates, with 8 technical replicates. ****, P < 0.0001 (unpaired t test). Error bars represent standard deviations. (b) Screening approach. J774A.1 macrophages were coincubated for 3 h with GRACE strains in the presence of 0.05 µg/ml DOX to repress target gene expression. Lysis events were determined by counting the number of propidium iodide foci. To detect whether a mutant has a significant defect in macrophage pyroptosis, we developed a model for host cell lysis in response to the wild-type strain using the locally weighted scatterplot smoothing method (LOESS) and evaluated each mutant relative to the model. Each dot represents an individual GRACE strain, with the calculated Z score shown. The grey dots represent strains with no significant difference from the wild-type results. Red dots represent strains with a significant decrease in induction of host cell lysis rates and a defect in filamentation. Black dots represent strains with a significant decrease in host cell lysis rates and no defect in filamentation. (c) Model for C. albicans interactions with macrophages. Blue lines represent cell surface moieties that are required for pyroptosis.
