FIG 1 .
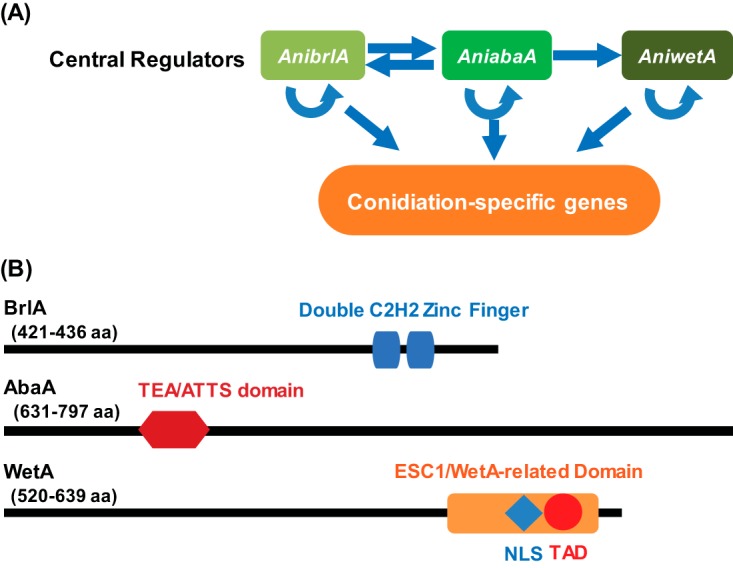
The central regulatory pathway of Aspergillus conidiation. (A) A cartoon depiction of genetic interactions of the central regulators in A. nidulans conidiogenesis. The central regulators cooperatively activate the conidiation-specific genes responsible for the morphogenesis of conidiophores. (B) The predicted protein architectures for the three conserved central regulators of conidiation in A. nidulans, A. fumigatus, and A. flavus. The blue box and the red hexagon represent the C2H2 zinc finger domain and TEA/ATTS domain in BrlA and AbaA, respectively, and were identified in a blastP (version 2.6.0) search (71). The red circle represents a putative transcription activation domain (TAD), which was predicted by 9aaTAD using the “Less stringent Pattern” setting (31), and in A. nidulans it has the amino acid sequence SEAALQAVR. The blue diamond represents the nuclear localization signal (NLS) predicted by NLStradamus using the 4 state HMM static model (32), and in A. nidulans it has the amino acid sequence KTKARREQEARDRRRK. The orange rectangle represents the ESC1/WetA-related domain (PTHR22934) predicted by the PANTHER classification system (72) and located at amino acids 497 to 547 in the A. nidulans protein.
