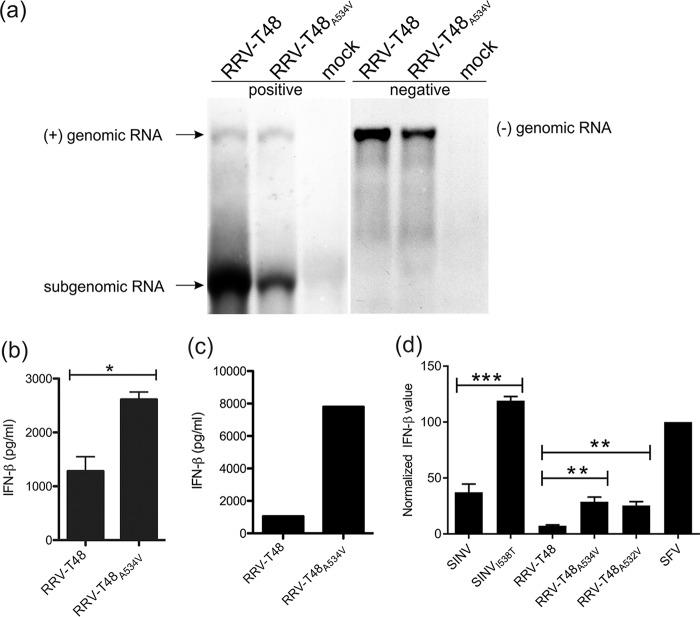
FIG 6 .
Replicases of RRV and SINV synthesize PAMP RNAs using cellular templates. BHK-21 cells were infected with RRV-T48 and RRV-T48A534V at an MOI of 1. At 6 h p.i., cells were lysed and total RNA was isolated. (a) Northern blot analysis was performed as described in the legend to Fig. 4b. Data from one of two reproducible independent experiments are shown. (b) One microgram of each RNA sample was used for transfection of Cop5 cells. The amount of IFN-β in the cell supernatant at 24 h p.t. was determined. IFN-β levels are expressed as means plus SEM from three independent experiments (*, P < 0.05 using Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test). (c) Poly(A)− fraction was obtained from isolated RNAs by removal of poly(A)+ RNAs, including viral dsRNA replication forms. One microgram of each RNA sample was used for transfection of Cop5 cells. The amount of IFN-β in the cell supernatant at 24 h p.t. was determined. Data from one of two reproducible independent experiments are shown. (d) Cop5 cells were transfected with plasmids designed to express wild-type and mutant forms of replicases of SFV, RRV, and SINV; the amount of IFN-β in supernatant was determined at 48 h p.t. Values obtained for cells transfected with RRV or SINV replicase expression plasmids were normalized to values obtained for cells transfected with plasmid expressing SFV4 replicase (taken as 100). Normalized values are shown as the means plus SEM from three independent experiments (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test).